In chemical engineering, distillation is one of the fundamental processes used to separate constituents of a mixture utilizing the difference in their boiling points. There are several distillation processes, but two are widely used – short path distillation and wiped film distillation. They help achieve efficient separation of compounds with minimal thermal degradation.
While both distillation methods are used in industries dealing with heat-sensitive materials and high-purity requirements, short path vs wiped film is a decision that often troubles producers. This article explores these advanced distillation methods and helps you understand their differences.
Sections
ToggleWhat is Short Path Distillation?
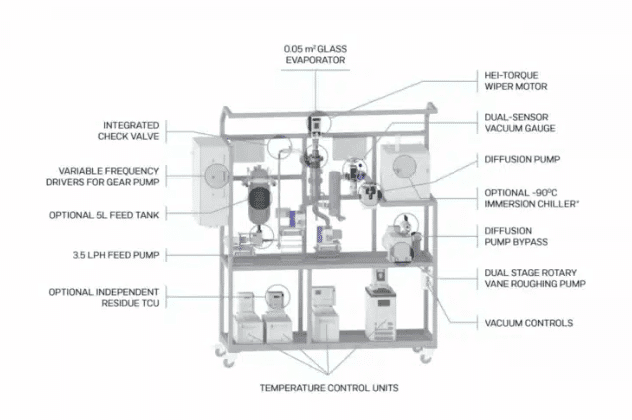
Short path distillation is a specialized technique to purify small quantities of high-boiling, heat-sensitive materials. This method is predominantly used in the lab setups as it has a short distance between the evaporator and the condenser. That’s why it is called “short path” distillation.
A typical short path distillation includes an evaporator (heated flask or vessel), a short-path condenser, and a receiving flask. Due to the proximity of the evaporator to the condenser, the process can work at lower operating pressures by reducing pressure drop. Heat is applied once the mixture is put in the evaporator, causing the more volatile components to vaporize. These vapors travel a short distance to the condenser, where they quickly condense and are collected in the receiving flask. The less volatile components remain in the evaporator.
What is Wiped Film Distillation?
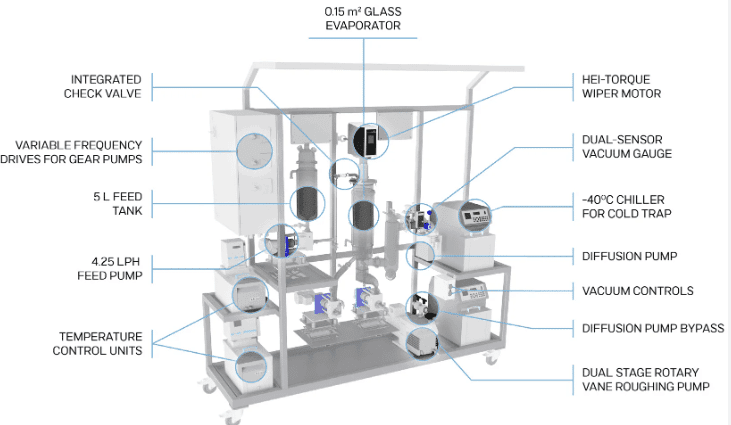
Wiped film distillation is also known as thin film distillation because it is a continuous distillation process that, using rotating wiper blades, spreads the mixture into a thin film on the heated wall of the evaporator. This distillation method separates heat-sensitive materials efficiently and at larger scales than short path distillation.
A wiped film distillation is made up of a cylindrical evaporator that has an internal heated surface. The rotating wiper blades ensure the film of the mixture flows down to vaporize the more volatile components, which are then quickly condensed in an internal condenser and collected in collection vessels. The key element in the setup is the set of wiper blades that continuously spread the feed material into a thin film on the heated surface.
Key Differences Between Short Path and Wiped Film Distillation

Aspect | Short Path Distillation | Wiped Film Distillation |
Efficiency | Efficiency High efficiency for small batches Excels at separating small quantities with high precision | Higher efficiency for larger volumes
Offers superior efficiency for industrial-scale operation |
Temperature Sensitivity | Excellent for highly heat-sensitive materials due to low pressure | Very good for moderately heat-sensitive materials may expose the material to slightly higher temperatures for a marginally longer time |
Scale and Throughput | Limited scalability, lower throughput, most suitable for lab setup | Highly scalable and higher throughput, preferred choice for industrial-scale operations |
Equipment and Maintenance | Simpler setup with fewer moving parts, resulting in easier maintenance | More complex setup with rotating parts (wiper blades) and a more intricate design, higher maintenance needs |
Advantages and Disadvantages
A comprehensive short path distillation vs wiped film comparison requires discussing the pros and cons of both processes.
Advantages of Short Path Distillation
- High Purity: Short path distillation is preferred for its high-purity distillates. It makes the process ideal for applications where product quality is the primary concern, such as pharmaceuticals and research. The short distance between the evaporator and condenser minimizes the risk of contamination.
- Simplicity of Setup: The setup for the short path distillation is relatively straightforward. Its equipment is designed to be easier to set up, operate, and troubleshoot. This simplicity makes the operation much easier in research settings or small-scale production facilities where versatility and ease of use are crucial.
- Ideal for Sensitive Materials: Short path distillation operates at very low pressures and minimal exposure to elevated temperatures. This makes this process exceptionally well-suited for processing heat-sensitive materials such as terpenes. It is advantageous for pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, where maintaining the integrity of delicate compounds is essential.
Disadvantages of Short Path Distillation
- Limited Scalability: One of the primary drawbacks of short path distillation is its limited ability to scale up for larger production volumes. Due to the short path between the evaporator and condenser, the size of the equipment is highly restricted, which makes it unsuitable for high-volume industrial applications.
- Lower Throughput: Short path distillation generally has a lower throughput capacity than wiped film distillation. The processing time is much longer for larger batches, potentially impacting production efficiency.
- Time-Consuming: The process, due to its limited size, can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with larger quantities of material. Producers may need to be processed in multiple runs.
Advantages of Wiped Film Distillation
- High Efficiency: Wiped film distillation offers unmatched efficiency, particularly for larger volumes of material, making it suitable for industrial applications. The continuous nature of the process makes it possible to process large batches in a short period.
- Better for Larger Volumes: The wiped film distillation equipment design can continuously process larger volumes of different kinds of material. This scalability is a significant advantage in industrial settings where high throughput is essential, such as cannabis processing.
- Consistent Product Quality: The continuous operation of the method offers precise control over process parameters. With wiped film distillation, producers can ensure consistent product quality. In industries such as cannabis extract processing, where batch-to-batch uniformity is crucial, this process offers a reliable distillation method.
Disadvantages of Wiped Film Distillation
- Higher Initial Investment: Wiped film distillation equipment is generally more complex and expensive due to its moving parts. It demands a higher initial investment than short path distillation setups.
- Complexity in Setup: The design of such a setup is more intricate, which adds complexity to setup and operation. Also, the complexity may require more specialized knowledge and training for operators, potentially increasing operational costs.
- Increased Maintenance Needs: Moving parts (such as the wiper blades) and a more complex overall design make wiped film distillation equipment challenging to maintain.
Which One Is Right for Your Company?
Choosing between wiped film and short path distillation depends on several factors. Here are the main selection criteria:
1. Product specifications and desired purity: The choice of the distillation method depends on the type of product and the purity required. Both methods are known for the purity they produce. Still, short path distillation is the better choice if you are working with highly heat-sensitive compounds or need the highest purity in smaller quantities. You can operationalize the short distillation process at low pressures and less cost.
However, if the materials you work with can tolerate slightly more thermal stress, you can use the wiped film process to achieve high purity at larger volumes.
2. Scale of operation and budget constraints: Make your choice based on the scale of the operation. The short-path distillation method is suitable for smaller-scale operations, laboratory settings, or the production of high-value, low-volume products. Due to lower initial investment costs, it can be ideal for small businesses that can function with limited scalability.
On the other hand, Wiped film distillation is the most suitable method for larger-scale, continuous operations. Compared to short path distillation, this method requires a higher initial investment. However, it offers better economies of scale for larger volumes.
3. Regulatory requirements and compliance: Another significant factor is the compliance requirement, which depends on your industry. Specific regulatory requirements related to your business can influence your choice of distillation method. For instance, validating and documenting the process thoroughly is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry. Both methods can meet high regulatory standards, but the choice may depend on which one aligns better with your existing quality control systems and documentation practices.
How can Root Sciences' combination of short path and wiped film help?
What if you can combine the purification levels of the short path distillation with the large-scale processing of the wiped film distillation?
Root Sciences has developed an innovative approach that combines the strengths of both short path and wiped film distillation techniques. The company’s wiped-film short-path distillation equipment offers several innovations and advantages over a short path or wiped film method when used individually:
1. Improved efficiency: By integrating short path and wiped film technologies, Root Sciences systems achieve a level of efficiency, surpassing what each method can offer individually. The equipment ensures high-purity initial separation, while the wiped film stage allows for efficient processing of larger volumes.
2. Reliability: The dual-method equipment is more reliable. Producers can work with volatile and heat-sensitive materials without degrading their quality, even on a large scale. Also, the design removes redundancy in separation stages and maintains product quality even if one component is not performing optimally.
3. Scalability: The limitation of the short path distillation to work at larger volumes and lack of wiped film distillation to achieve the same level of purity for all materials are addressed by Root Sciences equipment. The systems can be scaled more effectively to meet growing production needs without sacrificing product quality.
4. Purity and potency: The multi-stage process allows for finer control over the distillation parameters. The equipment is designed to separate susceptible compounds while refining the product. You can consistently maintain higher purity levels and potentially greater potency in the final product, which is particularly valuable in industries like pharmaceuticals and cannabis extraction.
Conclusion
The choice of short path vs. wiped film depends on several factors, including product specifications, scale of operation, budget, regulatory requirements, and operational considerations. Both distillation methods have distinct advantages; Root Sciences wiped-film short-path distillation equipment combines both approaches, offering a compelling solution that addresses many of the limitations of each technique.
Our solutions provide enhanced efficiency, reliability, scalability, and product quality, making it a versatile choice for companies looking to optimize their distillation processes across various applications and scales.




