The development in cannabis extraction methodologies has made it possible to produce potent and high-quality extract. Two of the most prominent extraction techniques widely used in the industry are ethanol extraction and supercritical CO2 extraction. This results in the debate on ethanol vs CO2 extraction CBD, which needs a closer understanding of how these extraction methods work, differ and affect the end products.
This article explores CO2 vs ethanol extraction, comparing their strengths and weaknesses, and aims to provide insight into which extraction technique best suits different scenarios.
Sections
ToggleUnderstanding Solvent-Based Extraction

Solvent-based extraction is also known as hydrocarbon extraction , as it typically uses a hydrocarbon as a solvent to separate desired compounds from plant material. In cannabis extraction, solvent-based methods are widely used for extracting cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant matter.
Common types of solvents used in the cannabis industry include:
- Ethanol
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Petroleum-based solvents (e.g., butane, propane)
- Other solvents like acetone or isopropyl alcohol (less common)
The key role of the solvents in the extraction process is to dissolve more volatile cannabinoids and terpenes, separating them from the plant material. Depending on the solvent, different compounds can be targeted for extraction, as well as the end product and overall efficiency.
What is Supercritical CO2 Extraction?

Supercritical CO2 extraction utilizes carbon dioxide in its supercritical state for cannabis extraction. In a supercritical state, CO2 exhibits properties of both a liquid and a gas, making it possible to target even the most sensitive terpenes and cannabinoids. The state occurred by heating CO2 at 31.1°C and pressurizing heated gas to 73.8 bar.
Compared to solvent-based extraction methods, CO2 extraction is more complex and uses specialized equipment to maintain the supercritical gas. The process of supercritical CO2 extraction works as follows:
- CO2 is pressurized and heated to reach its supercritical state in a specialized vacuum chamber.
- The supercritical CO2 is passed through cannabis plant material in an extraction vessel.
- As a solvent, CO2 dissolves the desired compounds from the plant material.
- The CO2-cannabinoid mixture is then separated in a collection vessel.
- CO2 is depressurized, returning to a gaseous state and leaving behind the extracted compounds.
- The separated CO2 is then pumped back into the system, making the whole process closed-loop.
Advantages of supercritical CO2 extraction
The cannabis industry is widely using the extraction method for several reasons:
- Clean and non-toxic method: CO2 is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA, which makes cannabis extraction non-toxic and less subject to strict scrutiny.
- Environmentally friendly: Unlike solvents, CO2 can be recycled in a closed-loop system, making the process sustainable.
- Precise: Allows for fine-tuning of pressure and temperature to target specific compounds.
- Preserves terpenes: Lower temperatures help maintain the integrity of heat-sensitive compounds.
Challenges of supercritical CO2 extraction
However, the benefits of the method also come with a set of challenges, including:
- High initial costs: Specialized CO2 extraction equipment is expensive and requires significant upfront investment.
- Longer processing times: The extraction process can be slower than other methods, such as solvent-based extraction.
- Technical expertise: This requires skilled operators to manage complex equipment and processes.
What Is Ethanol Extraction?
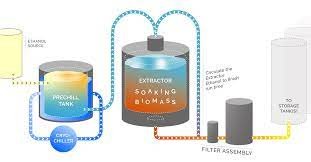
Ethanol extraction uses high-proof grain alcohol as a solvent to extract cannabinoids and other compounds from cannabis plants. Due to the easy availability of ethanol, the process is more economical than other extraction methods. Also, it is a comparatively more straightforward process.
The ethanol extraction process involves:
- Soaking the cannabis material in ethanol allows the solvent to dissolve target cannabinoids and terpenes.
- The solution of ethanol and cannabis compounds is filtered to separate the solvent from the plant material.
- Residual ethanol is then removed from the extract through evaporation or distillation.
- Depending on the quality of the final extract, further refinement may be done to remove unwanted compounds for purification.
Advantages of ethanol extraction:
- Highly cost-effective due to lower equipment costs and operational expenses.
- It is a more straightforward extraction process with no specialized equipment involved; it is easier to scale, making it fit for large-scale operations.
- Scalability makes the process versatile for both small and large-scale operations.
- Ethanol extraction is also more efficient, with faster extraction times than CO2.
Challenges of ethanol extraction:
- Potential for residual solvents making final purging necessary to ensure product safety.
- Loss of some terpenes as ethanol can extract water-soluble compounds, potentially affecting flavor profiles.
- The process can also dissolve chlorophyll, requiring additional post-processing to remove unwanted plant materials.
Ethanol Extraction vs. CO2

Factor | Ethanol Extraction | CO2 Extraction |
Efficiency | Fast processing times, high yields, best for large scale operations | Longer processing times, potentially lower yields |
Cost | Lower initial investment, cheaper operational costs, no specialized equipment required | High initial investment due to specialized equipment, higher operational costs |
Product Quality | Good purity, potential loss of some terpenes | High purity, better terpene preservation |
Environmental Impact | Renewable solvent, but energy-intensive distillation | Low impact, CO2 can be recycled |
Safety | Flammable, requires proper handling | Non-flammable, generally safer to handle |
Petroleum-Based Hemp Extraction: A Comparison

Petroleum-based extraction methods are similar to other solvent-based processes using hydrocarbons like butane or propane for separating cannabinoids and terpenes. However, petroleum-based hemp extraction is becoming less common due to safety concerns and regulatory scrutiny.
When we compare petroleum-based methods with ethanol and CO2, petroleum-based hemp extraction can be very efficient and yield high-quality extracts. Cost is also generally lower due to equipment costs than CO2, but higher than ethanol. However, these benefits are overshadowed by significant safety risks due to the flammability and explosiveness of the solvents.
Apart from safety concerns, there are several reasons why ethanol and supercritical CO2 extraction are preferred over petroleum-based methods. CO2 and ethanol are primarily safer for operators and consumers than petroleum solvents. For producers, there are fewer regulatory hurdles and more widely accepted practices. Also, the end products produce cleaner extracts with less risk of residual solvents.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Extraction Method
As a product, when deciding between ethanol extraction vs CO2, these are the factors you should consider:
- Business goals:
If you launch large-scale commercial operations, ethanol extraction may be more suitable due to faster processing times. However, CO2 extraction will be better for boutique quality products because of its ability to preserve terpenes and create high-purity extracts.
- Budget constraints and ROI:
Supercritical CO2 extraction systems require higher upfront costs but may offer long-term benefits due to CO2 recycling. On the other hand, ethanol extraction setup is cheaper to start and typically has lower ongoing expenses.
- Desired product characteristics:
Both extraction methods can produce full-spectrum cannabis products, but CO2 may better preserve the plant’s original profile. If you are targeting isolates, ethanol is often preferred for its efficiency, while CO2 can be fine-tuned to extract specific compounds, making it suitable for broad-spectrum products.
- Regulatory compliance and consumer expectations:
Check the local regulations, as they may favour one method. Some States have stricter requirements for residual solvents, favoring CO2 extraction. Additionally, the growing demand for “cleaner” cannabis products gives CO2 extraction a marketing advantage.
Ethanol Extraction vs CO2: Which One Is Better?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to CO2 vs ethanol extraction choice. Each extraction method has strengths; the choice depends on your budget, staffing, and product goals.
- CO2 extraction is for high-end, terpene-rich products where preserving the plant’s original chemical profile is crucial. Such products command premium prices in the market.
- Ethanol extraction is favored for large-scale operations where cost-effectiveness and throughput are primary concerns. Such products are cheaper in comparison.
- Both methods are viable for CBD extraction. Ethanol vs CO2 extraction CBD selection comes down to your requirements from the end product and the manufacturer’s resources.
- CO2 extraction may have an edge as consumers are particularly concerned about product purity and the absence of residual solvents.
- Ethanol extraction can be advantageous for companies looking to enter the cannabis industry quickly with lower initial investment.
Conclusion
Both ethanol and CO2 extraction methods are widely present in the cannabis industry. Each method offers distinct advantages and challenges, and choice depends on various factors, including budget, desired product quality, scale of operation, and target market.
While supercritical CO2 extraction can produce high-purity extracts with excellent terpene preservation, the process’s high initial costs and complexity can hinder smaller operations. On the other hand, ethanol extraction offers a more accessible entry point with lower costs and a more straightforward process. The process is more economical and simpler for large-scale operations but has risks of residual solvent. Ultimately, the decision to ethanol vs CO2 extraction should be based on carefully analysing your operations’ needs, resources, and goals.




