As the modern healthcare and wellness industry is moving towards holistic solutions, cannabinoids present an alternative. These fascinating compounds are one of the most important discoveries, and researchers have identified over 100 distinct cannabinoids to date. In this article, we explore what cannabinoids are and their types. We also discuss how these compounds have applications beyond recreational use and extend to human physiology and potential treatments.
As the diversity of cannabinoid effects has sparked a revolution in how we approach various medical conditions, from chronic pain to neurological disorders, it is helpful to have an understanding of cannabinoids.
Sections
ToggleUnderstanding Cannabinoids: The Basics
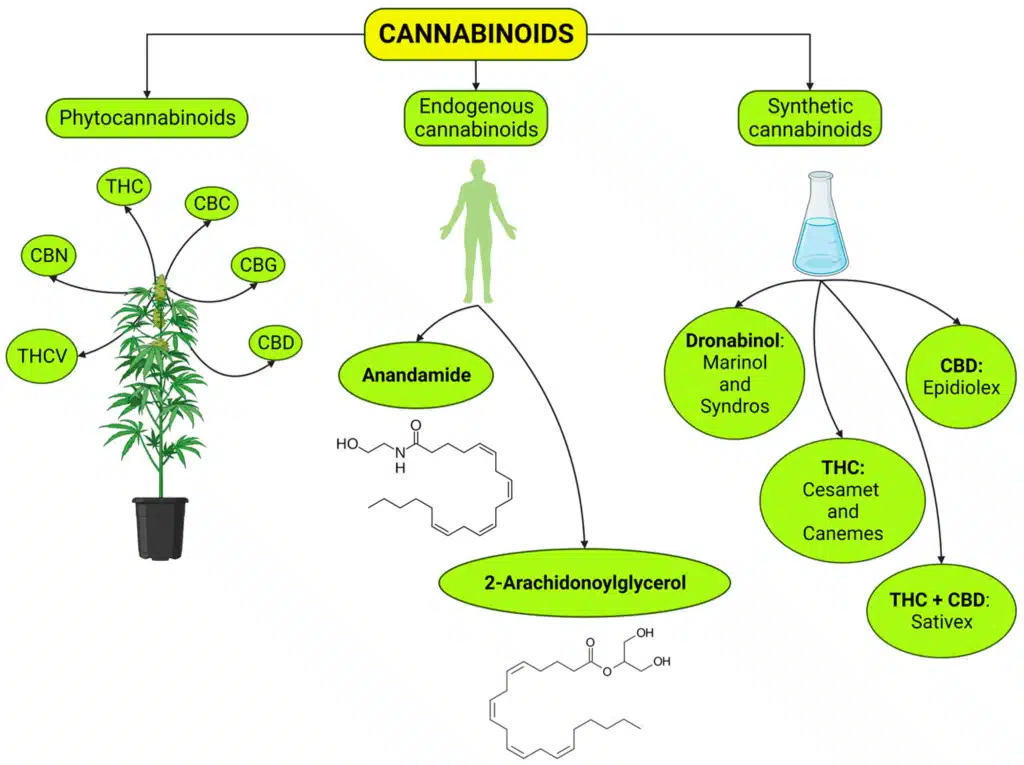
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring chemical compounds found in cannabis and other plants that can interact with specialized receptors. These bioactive molecules can be categorized into three main categories:
- Phytocannabinoids: These are plant-derived cannabinoids that are primarily found in cannabis. There are over 100 distinct types of cannabinoid sources from plants. THC and CBD are the most well-known examples.
- Endocannabinoids: Natural cannabinoids are also produced by the human body to help maintain internal hormonal balance. It includes anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
- Synthetic Cannabinoids: These are laboratory-created compounds designed to mimic natural cannabinoids’ effects, expanding the cannabinoids list for therapeutic research.
Cannabinoid Receptors
For a better understanding of what cannabinoids are, it is crucial to be familiar with the human body’s endocannabinoid system. Two primary receptor types facilitate cannabinoid effects on the body:
1. CB1 receptors are primarily in the central nervous, brain and spinal cord. The location of these receptors makes them impactful in controlling memory, mood, pain, appetite, and movement. CB1 receptors are the main target of the THC present in cannabis. By binding to these receptors, THC can produce psychoactive effects.
2. CB2 Receptors: Predominantly found in the peripheral nervous system, CB2 receptors are abundant in immune cells and tissues. Concentration in these areas makes these receptors crucial to inflammation and immune response. These receptors can be found in skin, bones, and various organs.
Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The ECS is a complex cell-signaling network that helps maintain bodily homeostasis. It presents a crucial ecosystem and defines how different cannabinoids interact with the body. The endocannabinoid system has several primary functions: mood regulation, pain management, appetite control, memory processing, and sleep regulation.
Types of Cannabinoids Explained
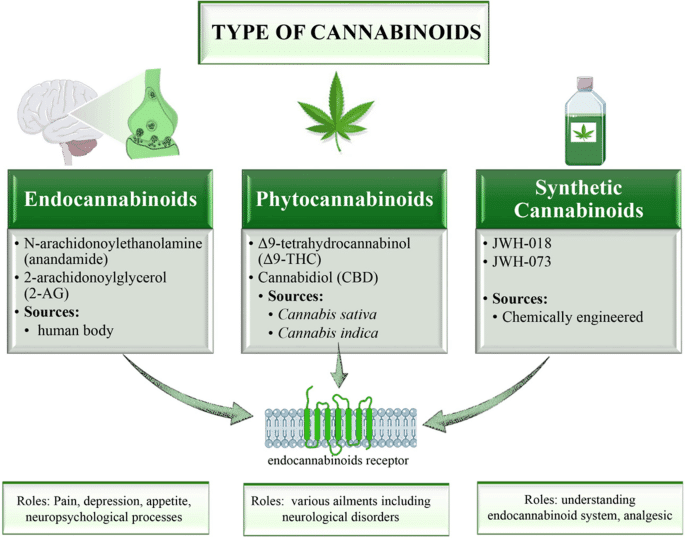
While there are over 100 cannabinoids identified, all the different types of cannabinoids can be categorized into one of the following main groups:
1. Major Phytocannabinoids: These are the most potent naturally occurring cannabinoids found in cannabis. The most common types of major phytocannabinoids include:
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): The primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, THC is the cannabinoid known to offer pain relief, appetite stimulation, and euphoric effects. It binds to the CB1 receptors in multiple forms, including THCA (acid form) and Delta-8 THC.
CBD (Cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound with widespread therapeutic potential. Due to its anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties combined with no risk of producing “high,” it is under study as a treatment for several medical conditions, including epilepsy, anxiety, and chronic pain.
CBG (Cannabigerol): Also known as the “mother cannabinoid,” it is a precursor to other cannabinoids. It demonstrates antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties and shows potential in treating glaucoma and inflammatory bowel disease.
2. Minor Phytocannabinoids: Minor phytocannabinoids have also been recently discovered and are being studied for their unique properties. Some of these compounds include:
CBC (Cannabichromene): A non-psychoactive compound with anti-inflammatory properties, CBC shows promise in pain management and neurogenesis.
CBN (Cannabinol): Another type of phytocannabinoid, CBN shows potential for pain relief and neuroprotection. However, it shows a mild psychoactive character created through THC oxidation.
CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid): A precursor to CBD, CBDA demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties and may help with nausea and anxiety.
3. Synthetic Cannabinoids: Synthetic cannabinoids are laboratory-created compounds that mimic natural cannabinoid effects. They are created to be more potent than natural cannabinoids. Some examples of synthetic cannabinoids include medications like Dronabinol and Nabilone.
Synthetic cannabinoids have varying regulatory status worldwide. Many synthetic cannabinoids are illegal, while others are approved for medical use. You must understand the regulatory challenges before using any such compound.
You need to be cautious while using synthetic cannabinoids due to their unpredictable effects due to varying potency and limited research on long-term effects.
4. Endocannabinoids: Another type of cannabinoids produced naturally by the body is called endocannabinoids. Two common endocannabinoids are:
Anandamide (AEA): Also known as the “bliss molecule”, it regulates mood, appetite, and pain sensation. It also plays a crucial role in memory and learning.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Another abundant endocannabinoid in the brain, 2-AG is critical for emotional state regulation. It also influences appetite and immune function.
How Do Cannabinoids Affect the Body and Mind?

Cannabinoids’ effects on the body are widely studied. There is ample evidence available connecting cannabinoids with body and mind.
Mechanism of Action
These compounds show effects on the body through multiple pathways. Cannabinoids like THC and CBD can directly interact with the body through direct receptor activation (CB1 and CB2). Another pathway is enzyme modulation, which results in digestive and pain relief management. For psychological benefits such as anxiety, stress, and memory, they act through neurotransmitter regulation. Furthermore, they also act through ion channel interactions, which are responsible for cell signalling and muscle contraction.
Psychoactive vs. Non-Psychoactive Effects
The impact of cannabinoids can be put into psychoactive and non-psychoactive effects.
Psychoactive Cannabinoids like THC have the following effects:
1. Mental Effects:
- Altered perception
- Modified thought processes
- Changed emotional states
- Enhanced sensory experiences
- Temporary memory changes
2. Physical Effects:
- Increased heart rate
- Red eyes
- Dry mouth
- Changed appetite
- Modified motor skills
Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoids
Non-psychoactive cannabinoids like CBD have the following effect:
- Therapeutic Benefits:
- Anxiety reduction
- Inflammation control
- Neuroprotection
- Pain relief
- Seizure management
- Physiological Effects:
- Blood pressure regulation
- Hormone balance
- Immune system modulation
- Sleep cycle regulation
Key Effects on Body Systems
Cannabinoids impact body systems on several levels. One of the main effects is pain management. These compounds result in nerve pain reduction, inflammatory pain control, chronic pain management, and acute pain relief. Another effect is inflammation control by reducing inflammatory markers, decreasing immune cell activation, and enhancing tissue repair.
Comparing Cannabinoids: What Makes Each Unique?
Let’s explore different types of cannabinoids to understand what makes them unique.
Cannabinoid Type | Chemical Properties | Primary Effects | Therapeutic Applications | Unique Characteristics: |
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) |
|
|
|
|
CBD (Cannabidiol) |
|
|
|
|
CBG (Cannabigerol) |
|
|
|
|
CBN (Cannabinol) |
|
|
|
|
Major Cannabinoids and Their Health Benefits

Now that we know how the major cannabinoids are unique, we will explore their health benefits and how they affect the body.
1. THC Benefits:
The most potent cannabinoid, THC, is known to influence the body in several ways. First, its psychoactive influence has a calming effect on the body. It is also known to help with chronic pain management in arthritis patients. Some other benefits include nausea reduction, sleep improvement, and PTSD symptom relief.
2. CBD Benefits:
Preferred for therapeutic application, CBD is chosen because, unlike THC, it doesn’t have psychoactive characteristics. It makes it safe for anxiety reduction and inflammation treatments without the risk of the entourage effect. It is also been studied for seizure control and potential cancer-fighting properties.
3. CBG Benefits:
Due to its antifungal and antibacterial properties, CBG is used in natural bacterial infection treatments. Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, it is used for glaucoma therapy and inflammatory bowel disease.
4. CBN Benefits:
This cannabinoid has sedative effects that make it suitable for insomnia management and anxiety reduction. It offers benefits, including sleep onset improvement, REM sleep regulation, and quality enhancement.
5. CBC Benefits:
Its anti-inflammatory properties help with digestive and joint inflammation. It has also shown anti-tumour potential in cancer cell growth inhibition, tumour size reduction, and metastasis prevention studies.
6. THCV Benefits:
It helps regulate appetite through appetite suppression, satiety enhancement, and blood sugar control. Given these benefits, it is used in weight management as it is known to help reduce fat cells and boost metabolism.
Health Benefits and Therapeutic Uses of Cannabinoids
Another area of cannabinoid application is the mental health treatment. There are scientific studies that provide evidence that cannabinoids can be used for anxiety and depression management. These compounds can be used for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), panic disorders, bipolar depression, and mood stabilization.
Neurological Applications
Studies show that cannabinoids can also help with neurological issues. These compounds have shown potential in epilepsy treatment related to Dravet Syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome. It can also be used for other neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis spasticity, Parkinson’s tremors, and Alzheimer’s symptoms.
Cannabinoids and Drug Interactions
Understanding how different types of cannabinoids interact with medications is crucial for safe and effective treatment. Before you use any cannabinoids, if you are on medication, your choice must be informed.
You must be aware of the risks of using blood thinner medications. In studies, cannabinoid interaction with anticoagulants like Warfarin has shown increased bleeding risk and altered INR levels. Also, interaction with anti-anxiety medications such as Benzodiazepines and SSRIs/SNRIs must be considered. If used in addition to these medications, cannabinoids can result in enhanced sedation, cognitive impact, disturbed serotonin level effects, and mood alterations.
All these interaction risks make it necessary to consult a healthcare provider before using any cannabinoids if you are on medication.
Different Forms and Methods of Consuming Cannabinoids
You can highly optimize the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids by understanding the various ways to consume different types of cannabinoids.
Product Types
1. Full-Spectrum Products: These cannabinoid products are full-spectrum because they contain all naturally occurring cannabinoids. These products include trace amounts of THC (≤0.3%) and have a high percentage of terpenes and flavonoids.
Due to natural compound preservation, full-spectrum products have maximum therapeutic potential and broader treatment scope.
2. Broad-Spectrum Products: These products feature multiple cannabinoid types and are often THC-free formulations. They preserve the original terpene profile and partial entourage effect. Due to their no psychoactive effect, they are risk-free and drug-testing-friendly.
3. Isolates: They are a concentrated form of cannabinoids with 99%+ purity with no additional compounds. Cannabinoid isolates are chosen for precise dosing for research applications, product formulation, and customized treatments.
Delivery Methods
Depending on the type of cannabinoid you choose, the delivery method also varies. With compounds like THC, vaping and smoking are the most efficient delivery methods. It offers rapid onset (2-3 minutes) and high bioavailability (50-80%). For compounds like CBD, oral consumption through edibles and tinctures is preferred. It has a delayed delivery onset (30-90 minutes), but the effects can be felt for an extended duration (6-8 hours). Oral consumption also makes for precise dosing and sublingual absorption. Also, topical applications such as creams and lotions offer localized effects requiring no systemic absorption.
Dosage Guidelines
Irrespective of the type of method or formulation, initial dosing should be low. Starting with a minimal effective dose with a gradual increase is the safest way. Also, the dosage must be based on body weight, medical condition, previous experience, and desired effects.
How Many Cannabinoids Are There?
Currently, there are at least 113 identified phytocannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant. Out of these natural cannabinoids, six are the most widely known – THC, CBD, CBG, CBC, CBN, and THCV. There are also 20+ minor cannabinoids with multiple variants of each type. Also, researchers have produced 300+ synthetic compounds using various pharmaceutical derivatives.
Safety, Legality, and Quality Control
The legal status of cannabinoids differs by region. In the United States, at the federal level, hemp-derived CBD is legal (<0.3% THC), while all marijuana-derived products are restricted. However, several states have legalized marijuana for medical programs.
Quality Control Measures
When choosing a cannabinoid product, always pay attention to its testing protocol. The report must provide information about potency verification, pesticide analysis, and heavy metal testing. Choose products that are manufactured with GMP-compliant practices.
Also, there is a high risk associated with the use of synthetic cannabinoids. Unregulated cannabinoids can have unpredictable effects and severe side effects such as psychosis, anxiety, and addiction potential.
Future of Cannabinoid Research and Industry Trends
With the study progressing and interest in cannabinoids growing, new research areas are emerging. There is a lot of interest in novel cannabinoid discovery and their therapeutic applications. Manufacturers are working on delivery system innovations and product formulation advances. One of the challenges remains in the context of regulatory evolution. With market expansion, there is a need for the legalization of cannabinoids, which can still be difficult for product development.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids and their effects have revolutionized the industry. Today, cannabis is more than a recreational element and is known to offer therapeutic and health benefits. The future of cannabinoid medicine looks promising, with ongoing discoveries and innovations shaping the field. We hope this comprehensive guide to what are cannabinoids demonstrates the complexity and potential of these compounds. Whether you are considering cannabinoids for medical or wellness purposes or recreational applications, knowledge of cannabinoid effects helps you make better choices.




