There are over 113 cannabinoids in a cannabis plant, and THC is the most discussed compound. Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are two other cannabinoids that play a significant role in cannabis product development.
In this article, we explore these two cannabinoids and discuss the difference between CBD and CBG. We also look at their origins, benefits, and potential applications in health and wellness.
Sections
ToggleWhat is CBD?

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants. It is particularly abundant in hemp varieties, making up to 40% of the plant’s extract along with THC. It was first isolated in 1940, and since then, it has been under research for product development for offering potential therapeutic properties without causing intoxication.
Extracted from the plant using methods such as CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction, and solvent extraction techniques, CBD has a diverse profile. The concentrated form is then further refined into various products. The chosen extraction method can affect the purity and potency of the final CBD product.
What is CBG?

Cannabigerol (CBG) is another non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. CBG is often called the “mother of all cannabinoids” because it’s the precursor from which other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC, are synthesized.
The prevalence of CBG is lower than CBD because it is present in much smaller quantities in mature cannabis plants. As the plant matures, the CBG is broken down by enzymes, which convert it to other cannabinoids. In mature cannabis plants, there is less than 1% CBG, while CBD can comprise up to 20% or more of the plant’s extract.
Key Differences Between CBD and CBG
Aspect | CBD | CBG |
Source (amount in plant) | Abundant quality found (up to 20% in some strains) | Scarce in mature cannabis plants (usually <1%) |
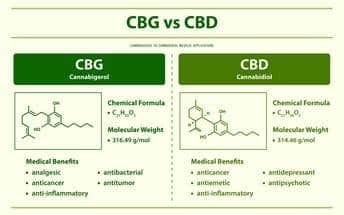
Chemical structure | C21H30O2 | C21H32O2 |
Interaction with endo cannabinoid system | Interaction is indirectly through CB1 and CB2 receptors | Direct interaction with CB1 and CB2 receptors |
Common products | Oils, tinctures, capsules, topicals | Oils, isolates, less common in other forms |
Therapeutic uses | Anxiety, pain, inflammation, epilepsy | Antibacterial, gut health, neuroprotection |
Therapeutic Benefits
Both CBD and CBG have extensive therapeutic benefits, including:
Benefits of CBD
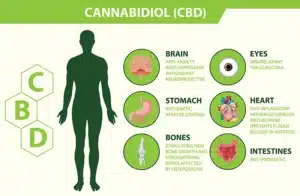
- Pain relief: CBD has shown promising results in managing various types of pain, including chronic pain conditions. Due to its interaction with the body’s endo cannabinoid system and other neurotransmitter systems, it can reduce pain perception and inflammation.
- Anxiety and stress reduction: CBD is particularly popular for its potential to alleviate anxiety and stress. In research, this cannabinoid has been found to interact with serotonin receptors in the brain, which play a crucial role in mood regulation.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: CBD’s anti-inflammatory effects come from its ability to reduce inflammation by interacting with the endo cannabinoid system and other inflammatory pathways.
It applies to conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and even skin conditions like acne and psoriasis. - Support for neurological conditions: One of the most recent breakthroughs in CBD research is treating certain neurological disorders. It is scientifically proven to help in neurological conditions such as epilepsy. That’s why the FDA has approved a CBD-based medication, Epidiolex, for treating specific forms of epilepsy.
Benefits of CBG
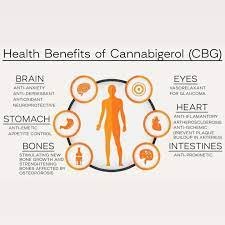
- Antibacterial effects: CBG has potential antibacterial properties, making it a possible antibacterial agent. Research has shown that CBG may be effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a bacteria resistant to many antibiotics.
- Support for gut health: What does CBG do for gut health? Several studies support the positive benefits of CBG on inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Potential neuroprotective properties: CBG may protect neurons from damage, potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Huntington’s disease. It makes CBG an essential compound in developing treatments for various neurological disorders.
- Emerging research on cancer-fighting properties: Studies on anti-tumour properties of CBG are still in the early stages but have shown that it may inhibit the growth of cancer cells, particularly in colorectal cancer.
Can CBD or CBG Cause a High?
No, unlike THC, neither CBD nor CBG produces psychoactive effects. THC produces the psychoactive effects by binding with the CB1 receptors of the endo cannabinoid system. On the other hand, CBD cannot directly interact with the CB1 receptors. It interacts with the endo cannabinoid system through other pathways. CBG interacts with CB1 receptors but at a much lower affinity level, producing no high.
Due to their benefits without causing intoxication, CBD and CBG are appealing to those seeking potential health benefits without altering their mental state.
Are CBD and CBG Legal?
Region | CBD Legal Status | CBG Legal Status | Key Notes |
United States | Federally legal if derived from hemp (<0.3% THC) | Federally legal if derived from hemp (<0.3% THC) | State laws may vary |
Canada | Legal | Legal | Only legal if follows Health Canada guidelines |
European Union | Legal if THC <0.2% | Legal if THC <0.2% | Regulations may vary by country |
United Kingdom | Legal if THC is <1 milligram | Legal if THC is <1 milligram | Must be sold as a nutritional supplement |
Australia | Legal with prescription | Legal with prescription | Products with less than 150 milligrams of CBD per day are available over-the-counter from pharmacists |
Asia | Varies by country | Varies by country | Generally, more restricted |
India | Illegal | Illegal | Except for medical and scientific use |
Africa | Varies by country | Varies by country | Some countries allow hemp-derived products |
Safety and Compatibility
A common concern among consumers is whether it is safe to take CBD and CBG together. Yes, it is safe to use these cannabinoids in combination. If you are looking for a slight entourage effect along with therapeutic use, then taking these cannabinoids may work more effectively in combination. CBD and CBG might offer enhanced benefits due to their complementary properties.
Still, due to limited research on the effects of specific combinations, users should start with low doses when combining cannabinoids.
Potential Side Effects:
Due to their minimal or no psychoactive properties, both CBD and CBG are generally well-tolerated. However, some users may experience mild side effects such as fatigue, changes in appetite, or digestive issues. The highest risk for pregnant or nursing individuals and those taking medications, as cannabinoids can interact with certain drugs.
The Difficulty of Producing CBG
As mentioned, the production of CBG cannabis is challenging due to its low concentration in mature cannabis plants. Harvesting young plants will result in a high concentration of CBG but with a poor terpene profile.
Cultivators must harvest plants early to optimise the concentration of CBG and terpenes or use specialized breeding techniques to increase CBG yield. This difficulty in production contributes to the higher cost and limited availability of CBG products compared to CBD.
How CBG and CBD Interact with the Body
Understanding how CBD and CBG interact with the body will help you appreciate their potential therapeutic benefits. Both these cannabinoids primarily interact with the body’s endo cannabinoid system but in distinct ways.
The endo cannabinoid system is a complex cell-signalling system that regulates various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and immune function. It consists of endo cannabinoids (cannabinoids produced by the body), receptors, and enzymes.
CBG interacts with CB1 receptors by acting as a partial agonist. This means it can bind to and activate these receptors but with less potency than THC. The same happens with CB2 receptors, mainly in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells. Unlike CBG, CBD doesn’t bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors. Instead, this cannabinoid modulates the ECS indirectly by influencing the activity of enzymes that break down endo cannabinoids and altering other compounds’ binding to these receptors.
Conclusion
A comparison of CBG vs. CBD requires understanding their origin, potential benefits, and ease of production. CBD remains a more mainstream cannabinoid, but CBG is also emerging as a compound of significant interest. The difference between CBD and CBG lies in their chemical structure, prevalence, interactions with the body, and potential therapeutic applications. The choice between CBD and CBG – or using them in combination – depends on individual needs and responses.




