Hemp oil is crucial in several industries, such as oil, food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Also, the increasing understanding of its potential health benefits and versatile applications is furthering its growth in the cannabis industry. If you are exploring hemp oil extraction, this guide is for you.
Here, we will explore the commercial process of extracting oil from hemp, explain various extraction methods, discuss the challenges faced in production, and discuss the science behind creating high-quality hemp extract oils.
Sections
ToggleWhat is Hemp Oil Made Of?
Hemp oil is a highly potent blend of several compounds that result in benefits. So, what is hemp oil made out of? The chemistry of the hemp plant is complex as it contains a variety of beneficial compounds, the most potent of which are:
- Cannabinoids: The primary active compounds in hemp and cannabinoids present include CBD (cannabidiol) and trace amounts of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Cannabinoids are the compounds that interact with our body’s endocannabinoid system, offering various therapeutic and recreational effects.
- Terpenes: These aromatic compounds contribute to the flavor and scent of hemp oil. Not unique to hemp, terpenes are found in almost every plant and are responsible for their distinctive aromas. However, hemp terpenes work synergistically with cannabinoids to enhance their effects, a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.”
- Essential Fatty Acids: Hemp oil is one of the few oils to contain a balanced ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, making it nutritionally valuable. These fatty acids are crucial for various bodily functions, including heart health, brain function, and inflammation regulation.
Hemp Seed Oil vs. Hemp Extract Oil
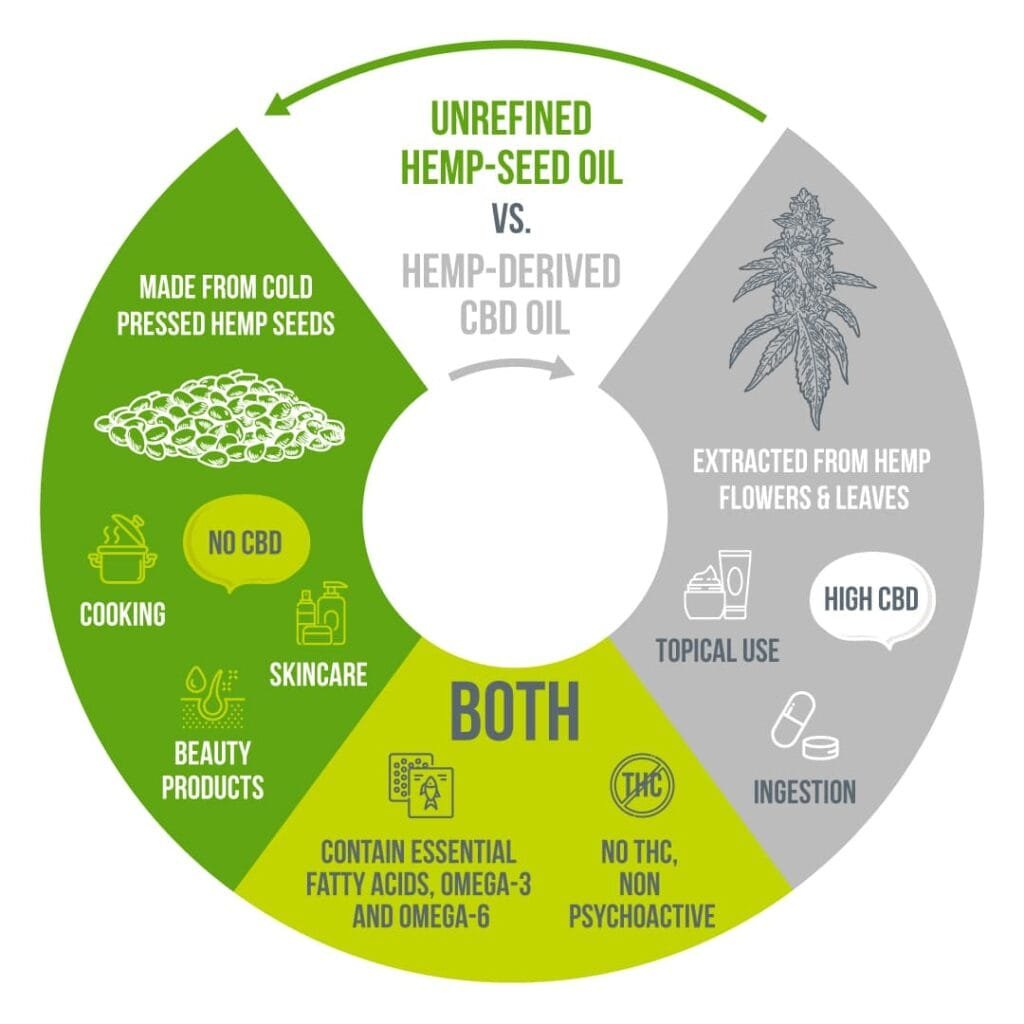
Hemp oil is a general term that can include hemp seed oil and hemp extract oil. However, there are differences you should know.
- Hemp Seed Oil: As evident, it is derived from hemp seeds, making it rich in nutrients, but hemp seed oil contains negligible cannabinoids. It is primarily used for its nutritional value and in cooking. Do not confuse hemp seed oil with CBD-rich hemp extracts, as one offers nutritional value while the other has potential therapeutic benefits.
- Hemp Extract Oil: Also known as CBD oil, this is extracted from the flowers, leaves, and stalks of the hemp plant. Hemp extract oil has a high concentration of cannabinoids, offering potential therapeutic benefits, and is the focus of most hemp oil extraction processes.
The Process of Extracting Hemp Oil: Step-by-Step Guide
The process of extracting oil from hemp involves several crucial steps. While there can be several extraction methods, the steps involved in producing high-quality hemp extract oils include:
- Harvesting & Drying: The process of extracting oil begins in the fields where hemp plants are carefully cultivated. Harvest time is crucial as plants should be harvested when cannabinoid levels peak. After harvesting, hemp is dried to preserve the cannabinoid content while reducing moisture. It is necessary to prevent mold growth.
- Grinding & Preparation: Properly dried hemp plant is then ground into a fine consistency. Grinding increases the surface area of the plant material, making the extraction process more efficient.
- Extraction: The core hemp oil extraction step can involve various methods to separate the desired compounds from the plant material. The choice of extraction method, such as solvent-based or solventless extraction, can significantly impact the hemp oil’s quality, purity, and composition.
- Filtration & Purification: After extraction, the raw hemp oil extract undergoes filtration to remove plant matter and other impurities. This process may involve materials such as activated charcoal or silica to produce a clean, pure extract while preserving the beneficial compounds.
- Winterization & Decarboxylation: More advanced filtering options are added if further purification is needed. Winterization is a process used to remove unwanted substances like waxes and lipids from the extract. It involves mixing the hemp oil with alcohol and freezing it, causing fats and lipids to solidify for easy removal. Decarboxylation, conversely, is a heating process that converts cannabinoid acids (like CBDA) into their active forms (like CBD).
- Final Testing & Packaging: Refined oil undergoes rigorous quality testing for potency, purity, and the presence of any contaminants before packaging. Once the oil passes all quality checks, it’s packaged in airtight, light-resistant containers to preserve its potency and freshness.
Different Methods of Hemp Oil Extraction
An extract can take several approaches to how hemp oil is made. Each method offers advantages and challenges that must be considered before choosing. Let’s take a closer look at the most widely utilized hemp oil extraction methods:
1. Solvent-Based Extraction

This extraction method uses solvents like ethanol or hydrocarbons (e.g., butane, propane) to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from hemp. Solvents are highly efficient at dissolving desirable compounds, which are then separated from the plant material.
Pros:
- High efficiency and yield, suitable for large-scale production
- Relatively low cost for setup and operation compared to some solventless extraction methods
- Can target specific compounds in hemp
Cons:
- Residual solvents are a challenge
- Safety concerns due to flammable solvents
- It may extract unwanted compounds like chlorophyll
2. CO₂ Extraction
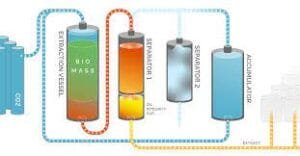
This extraction method uses pressurized carbon dioxide to extract compounds from hemp. It uses CO2 in supercritical and subcritical states, offering a cleaner extraction method.
Supercritical CO2: This process uses CO2 above its critical point (31.10°C and 7.38 MPa), exhibiting the properties of both a liquid and a gas. In this state, CO2 efficiently penetrates plant material and dissolves various compounds.
Subcritical CO₂: In this method, CO2 is used at lower pressure and temperature, making it helpful in extracting temperature-sensitive compounds. Supercritical extraction is less efficient but produces cleaner extracts.
Pros:
- Produces clean, high-quality extracts with no residual solvents
- Highly tunable process for extracting specific compounds from hemp
- CO2 extraction is environmentally friendly and sustainable
Cons:
- Requires high initial equipment cost
- Requires trained staff to operate specialized equipment
- Due to the use of heat, it may not be as efficient for extracting certain compounds
Click Here to Know More about Sub & Supercritical Cannabis CO2 Extraction Equipment
3. Oil Infusion Method

It is a traditional extraction technique that involves heating hemp in a carrier oil (like olive or coconut oil) to extract cannabinoids and terpenes.
Pros:
- Simple and accessible for small-scale or home production
- No special equipment is required
- Produces a full-spectrum extract with a complete terpene profile
Cons:
- Lower efficiency compared to other methods
- Difficult to scale for commercial production
- Low consistency in the final product
4. Steam Distillation

This method uses steam to extract volatile compounds from hemp. High-pressure steam vaporizes the volatile compounds, which are then condensed and collected.
Pros:
- No solvent residues in the final product
- Suitable for highly pure extracting essential oils and terpenes
- Simple setup compared to more advanced methods
Cons:
- Not helpful in extracting volatile cannabinoids
- Requires high temperatures
- The time-consuming process is not suitable for large-scale production
Best Extraction Process: Which One to Choose?
Depending on your business goals, let’s refine each hemp oil extraction method. It will make the choice of the best hemp oil extraction method easy.
- Yield: If you prioritize high yield, any solvent-based extraction method, including CO2 extraction, is ideal as it offers the highest yields. In commercial production setup, CO2 extraction can yield up to 95% of the available cannabinoids. Oil infusion and steam distillation typically have lower yields, often around 50-70%.
- Purity: CO2 extraction and steam distillation produce the cleanest extracts, free from residual solvents. These are the ideal extraction methods for making products for medical use or for consumers concerned about purity.
- Cost: While CO2 is efficient and produces high-quality results, it has a high initial cost, often ranging from $100,000 to $500,000 for commercial-scale equipment. If cost is a significant concern, solvent-based hemp oil extraction methods are more cost-effective, with setup costs typically between $10,000 and $100,000.
- Scalability: Solvent-based methods are highly scalable, making them suitable for industrial production. These methods can be easily adjusted to handle larger volumes as demand grows.
Upgrade your extraction process with Root Sciences.
Post-Extraction Refinement & Filtration
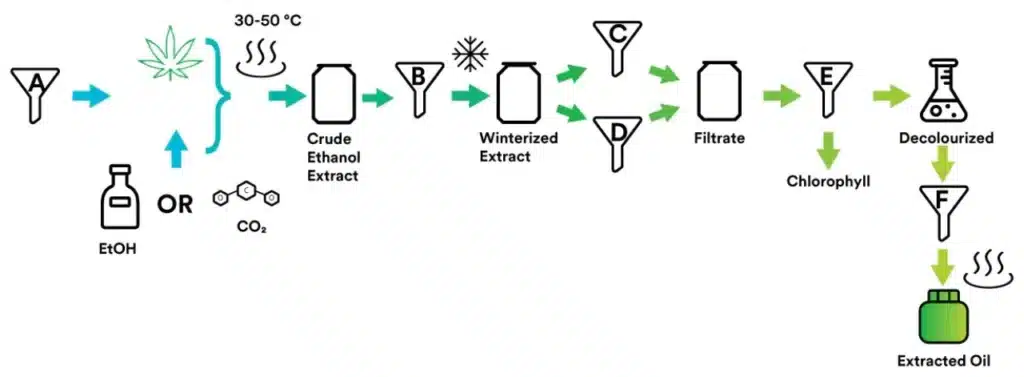
After the initial extraction, hemp oil extract may require several refinement processes to improve its purity and potency. Here are the widely utilized refinement and filtration methods:
1. Winterization: This process uses ethanol to remove unwanted waxes, lipids, and chlorophyll from hemp oil. In winterization, hemp oil is dissolved in ethanol and frozen to solidify unwanted substances. Solidified extracts are filtered out, leaving a purer extract.
2. Decarboxylation: Raw hemp extract contains cannabinoids in their acidic forms (e.g., CBDA, THCA). Applying heat breaks their carbon bond (decarboxylation), converting them into active forms (CBD, THC). The timing and temperature in this process are crucial, as overheating can degrade the cannabinoids.
3. Filtration: Various filtration methods are used to further purify the hemp oil extract, particularly for medical applications. This may include:
- Activated charcoal filtration to remove chlorophyll and other impurities
- Silica gel chromatography for isolating specific compounds
- Molecular distillation to separate compounds based on their boiling points
Depending on the intended use, any of these refinement processes can produce high-quality hemp extract oils.
Common Challenges & Quality Control in Hemp Oil Extraction
Hemp oil extraction also involves challenges that extractors should understand. It will help them overcome these challenges and meet quality requirements.
1. Regulatory Compliance: Due to the tight regulation around hemp products, hemp extract oils are also heavily regulated, requiring strict adherence to THC limits (typically 0.3% or less) and quality standards. How hemp oil is made legally in facilities includes careful strain selection, precise extraction processes, and regular testing.
2. Contamination Risks: Hemp oil in any form must be pure to offer therapeutic, nutritional, or recreational benefits. Producers must ensure the final product is free from pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial contaminants. This requires careful control throughout the entire hemp oil extraction process, from cultivation to final packaging.
3. Efficiency vs. Cost: From a business point of view, balancing the need for efficient extraction with cost-effective production is an ongoing challenge. Extraction methods like CO2 extraction offer high efficiency and purity but incur significant upfront costs. Producers should choose the appropriate extraction method considering their target market, production volume, and available resources.
Conclusion
Hemp oil is a fascinating blend of compounds with applications in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and several other industries. For extractors, hemp oil extraction can be a profitable venture, provided they have a proper understanding of hemp extract oil and the process of creating high-quality hemp oil.
As we’ve explored, there are multiple ways to extract oil from hemp, each with advantages and challenges. There are several methods, from traditional solvent-based methods to advanced CO2 extraction. The choice depends on purity, cost, and type of product. As demand for hemp extract oils continues to grow, further advancements in extraction techniques are expected. Whether you’re a consumer, producer, or simply curious about the process, understanding the science and art behind hemp oil extraction can deepen your appreciation for this versatile and potentially beneficial product.




