In the cannabis and hemp industry, two products or rather classes of products that often cause debate is the THCA vs CBD comparison. Both are cannabinoid content sourced from cannabis plants, but they have distinctive characteristics and significantly vary in how they affect the human body.
To help you better understand the differences, we have created this detailed THCA vs CBD comparison guide. Here, we will explore the chemical structures, potential benefits, and legal status of each cannabinoid.
Sections
ToggleWhat is THCA?
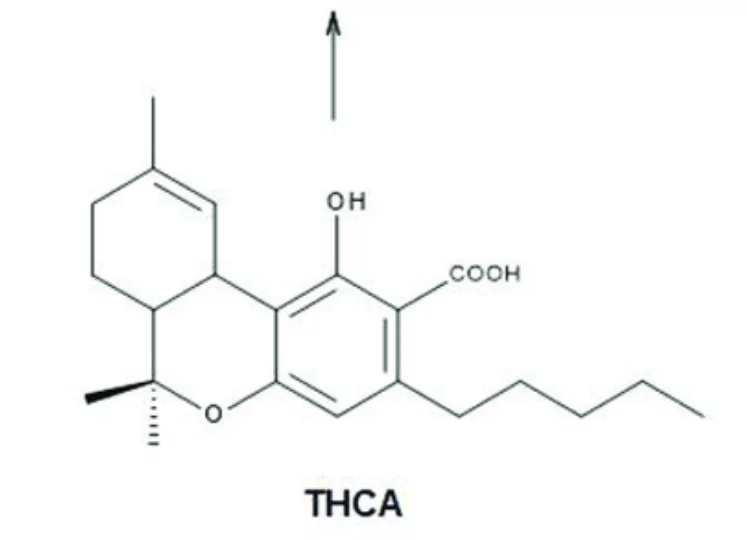
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid sourced from a live cannabis plant. It is most famous as the precursor to THC, which is the compound that gives cannabis its “high” character.
THCA is abundant in nature, and it is present in cannabis plants in high quantities. However, it has no psychoactive character until heat is applied. When THCA is heated, it undergoes decarboxylation, which converts it to THC. That’s the reason why raw marijuana has no psychoactive effects, but when vaped or smoked, it produces a high. To explore more about the cannabis distillation process and THCA extraction, visit this blog post on THCA distillate.
What is CBD?
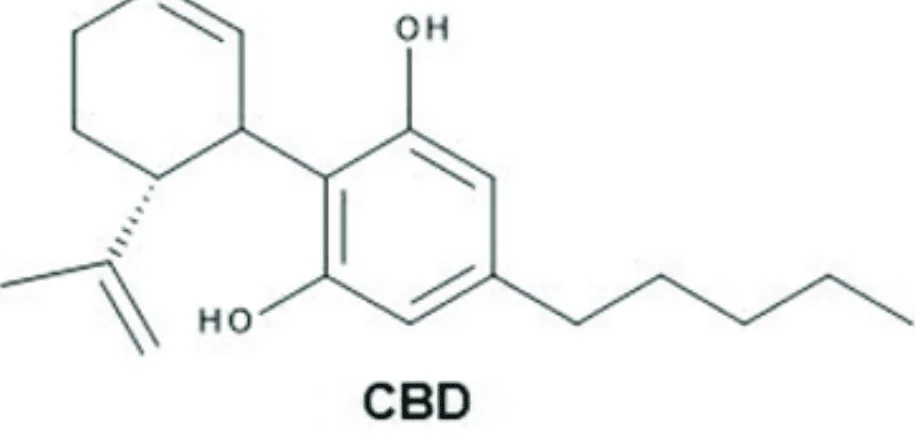
CBD, or simply cannabidiol, is another commonly occurring cannabinoid in cannabis and hemp plants. The main difference between THC and CBD is that it is a non-psychoactive compound. No “high” feeling is produced, irrespective of how it is used. Still, CBD has gained popularity in recent years because of its potential therapeutic properties. Also, in many countries, CBD is legalized for its health benefits in the absence of any psychoactive effects, as opposed to THC.
CBD can interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) and offer potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic properties.
THCA vs. CBD: Key Differences
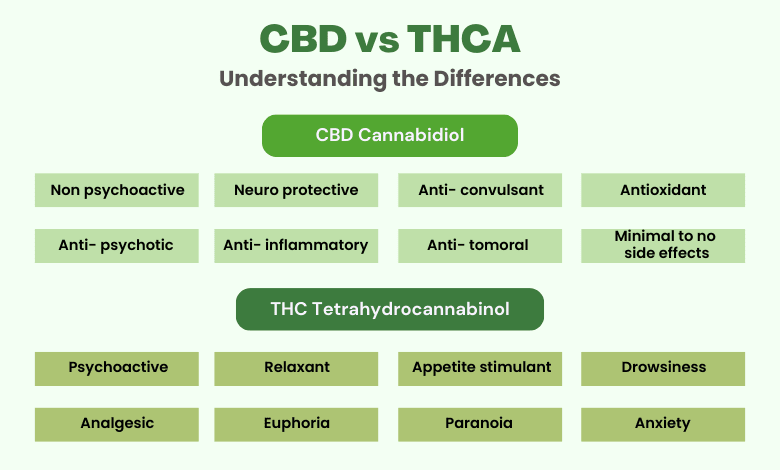
A lot of differences exist between CBD and THCA, but as a producer or enthusiast, there are some aspects that you must primarily focus on. While both are cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, here are the key differences between the two:
Aspect | THCA | CBD |
Psychoactivity | Highly rich in THC but Non-psychoactive in raw form | Non-psychoactive compound with no THC |
Legality | Legal status varies between states; often restricted | Legal in many countries when derived from hemp |
Source | Primarily found in raw cannabis | Common in both cannabis and hemp plant |
Therapeutic Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antiemetic | Anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, analgesic |
Interaction with ECS | Indirect interaction by affected the central nervous system | Direct interaction with CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system |
Conversion to THC | Converts to THC when heated due to decarboxylation | Does not convert to THC |
How Does THCA Work?
Cannabinoids affect the body by directly interacting with the CB1 and CB2 receptors. However, due to its unique chemical structure, THCA cannot directly interact with these receptors. It is found to interact with the endocannabinoid system through other mechanisms. One way it offers benefits is by providing anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting certain enzymes and proteins involved in inflammation. Additionally, THCA vs. CBD research indicates that THCA has neuroprotective effects that can potentially benefit conditions like Parkinson’s disease. When smoked or vaped, THCA converts to THC, which is a highly psychoactive cannabinoid capable of directly affecting ECS.
How Does CBD Work?
CBD can directly interact with the endocannabinoid system. However, it doesn’t interact in the same manner as THC affects the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Studies have termed CBD’s mechanism of action as complex and not fully understood, but it is believed to modulate various neurotransmitter systems in the body. CBD has been found to directly influence serotonin receptors, resulting in anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. It also impacts other receptors involved in pain perception and inflammation.
Potential Benefits of THCA

THCA is not only a recreational cannabinoid but is also used for its medicinal and therapeutic benefits. It includes:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: THCA can block the production of enzymes and proteins that cause inflammation. It can benefit conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Neuroprotective effects: Some studies suggest THCA could protect brain cells from damage and degeneration because it can penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and affect the central nervous system.
- Appetite stimulation: THCA may help with chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) by limiting the hormone leptin and suppressing appetite. It can be beneficial for individuals undergoing chemotherapy or suffering from eating disorders.
- Antiemetic effects: Extending the same benefits, THCA has shown potential in reducing nausea and vomiting, particularly in cancer patients undergoing treatment.
- Pain relief: Due to its analgesic properties, research indicates that THCA can relieve chronic pain conditions.
Potential Benefits of CBD
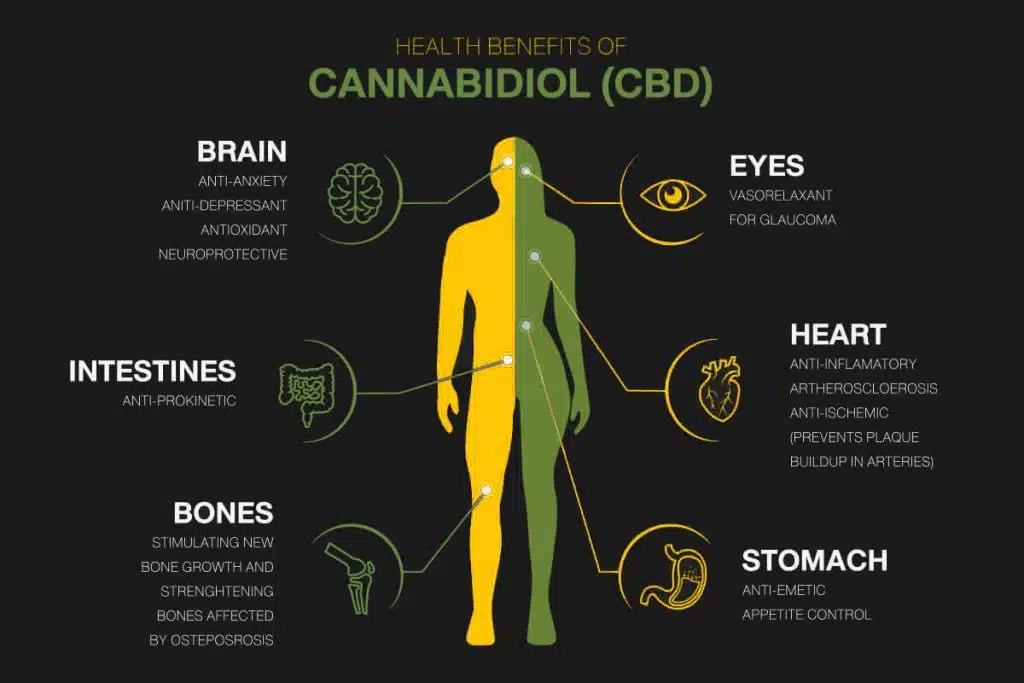
CBD is more extensively used for medical and therapeutic applications due to its potential benefits, which include:
- Anxiety relief: By interacting with the nervous system, CBD has shown promise in reducing symptoms of anxiety disorders and promoting relaxation.
- Seizure reduction: CBD has been approved by the FDA for treating certain forms of epilepsy in children, such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome. Researchers have termed its “comparatively favorable therapeutic index and the probable lower incidence of undesirable psychoactive properties” suitable for children.
- Sleep aid: CBD products are widely used for improving sleep quality and duration without any side effects or addictions because of their calming effect on neurons.
- Heart health support: CBD may have cardiovascular benefits beyond mental benefits, including reducing blood pressure and improving circulation.
- Skin health improvement: Topical CBD products are becoming common as CBD has shown potential to treat acne, psoriasis, and other skin conditions.
Does THCA Make You High?
No, THCA is not psychoactive in its raw form. That’s why you don’t get high by simply smelling or chewing on buds or leaves. This is because THCA has a different molecular structure than THC, which prevents it from binding effectively to the CB1 receptors in the brain responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis. The “high” effect comes from THC, which is produced when THCA is heated.
Side Effects: CBD vs. THCA
An insightful CBD vs THCA comparison is not complete without considering the potential side effects of these cannabinoids.
Both CBD and THCA are generally well-tolerated, but some users may experience mild side effects such as fatigue, changes in appetite, or diarrhea. The World Health Organization has termed CBD safe for use and less likely to have abuse side effects. However, it can still interact with certain medications, and medical consultation with a healthcare provider is mandatory.
THCA, in its raw form, is non-psychoactive, but information on its long-term effects is limited. When THCA is converted to THC, it can produce several side effects, including:
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
- Impaired memory
- Increased heart rate
- Feeling high
- Slower response rate
Drug Testing: CBD vs. THCA
Drug testing must be considered before using any cannabis-derived products. CBD vs THCA drug testing results can vary significantly.
Pure CBD has no THC content and should not result in a positive drug test for THC. Most drug tests are not designed to detect THC. However, pay attention while using CBD products as some may contain traces of THC, potentially triggering a positive result in drug tests.
THCA, on the other hand, can be more problematic for drug testing. While raw THCA is not psychoactive, it is volatile and can convert to THC when exposed to heat or light. It means even if you consume raw THCA, it could potentially lead to a positive THC drug test as the THCA can convert to THC in the body or during the testing process.
Another vital consideration in this context is whether CBD contains THCA. While CBD derived from most sources has no THCA, those derived from marijuana might.
Choosing Between THCA and CBD
The choice between THCA and CBD depends on your circumstances and use objective. For those seeking potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids without any risk of psychoactive effects, CBD is the most suitable choice for them. At the same time, those who seek more robust medical benefits, like cancer patients, can explore THCA. However, THCA will convert to THC when heated, which may not be desirable for everyone.
People often ask, “Is THCA like CBD,” the answer is complex. Both are cannabinoids and offer potential therapeutic benefits without psychoactive effects in their raw forms. However, CBD enjoys a more generous legal status and offers much more safety when drug testing is involved.
Conclusion
While THCA and CBD are cannabinoids, they offer unique properties and potential benefits. CBD is the most extensively used cannabinoid and, thus, widely available. THCA, on the other hand, is gaining attention for its possible therapeutic applications in its raw form, but its legal status is still disputed.
When making the THCA vs CBD decision, understand the differences, benefits, and side effects to make informed decisions about their use.




