For most people familiar with cannabis products, THC is a known compound. Most consumers choosing cannabis for recreational purposes look at THC content before selecting a product.
But what about THCA?
A cannabinoid closely related to THC, THCA has distinct properties and effects on the human body. In this article, we explore the key differences between THCA and THC. We look at their origins, chemical structures, benefits, and how they function.
Sections
ToggleCannabinoid Basics: THC and THCA

Cannabinoids are the naturally occurring compounds in the cannabis plant that provide their unique properties. These compounds have a chemical structure enabling them to interact with the human endocannabinoid system, influencing various physiological processes.
While there are several kinds of cannabinoids, THC and THCA are the two most studied and discussed. THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the main ingredient of any cannabis product known for its psychoactive effects.
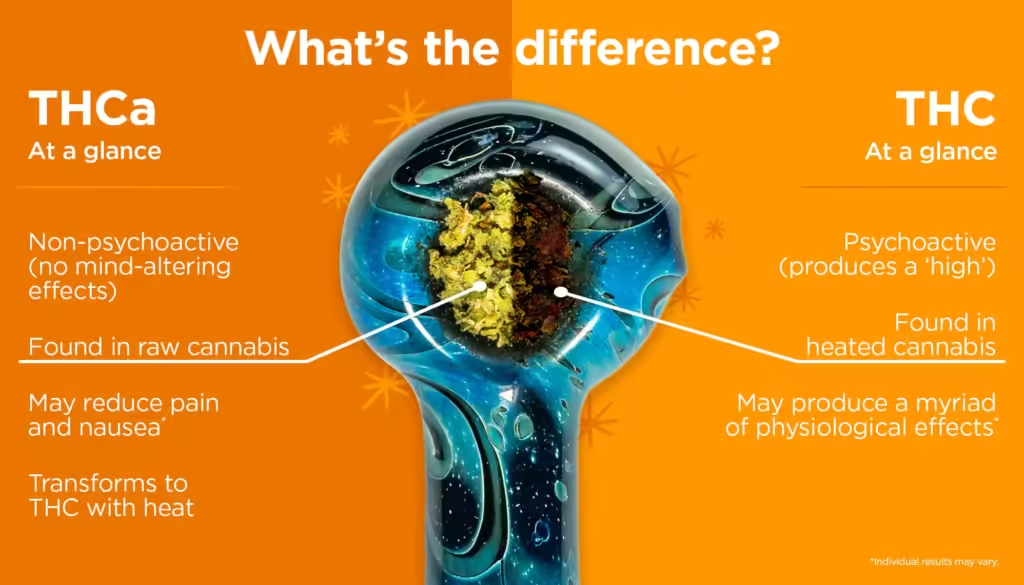
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive precursor of THC. While highly rich in THC, THCA doesn’t show any psychoactive characteristics until heated, which converts it to THC.
Both compounds have unique properties that contribute to the complex effects of cannabis on the human body.
Origin in the Cannabis Plant
There is a drastic difference between THC and THCA, even when both originate from the same source – the cannabis plant.
THCA is produced within the trichomes of the raw cannabis plants as they grow and mature. THCA is present in fresh, unheated cannabis, and it is often a source of therapeutic effects. As the cannabis plant dries and ages, the THCA present in the trichomes is slowly exposed to heat, converting to THC. Natural THCA is not psychoactive and has no “high” effect until heat is applied to convert it to THC.
This process is best illustrated when fresh or dried cannabis is smoked. It accelerates the conversion of THCA to THC, causing a “high.”
Chemical Structure and Properties
The THCA vs THC comparison is complete, with the chemical composition discussed. The difference between THCA and THC lies primarily in their molecular structure.
THCA has an extra carboxyl group (COOH) attached to its molecule compared to THC. While seemingly a small molecular difference, it significantly changes their chemical properties and how they interact with the body. Due to an additional carboxyl group, the THCA molecule is more significant and unable to fit into the cannabinoid receptors in our brains. This is the reason why THCA doesn’t produce psychoactive effects. THC, on the other hand, due to its lack of extra COOH, fits perfectly into cannabinoid receptors, leading to the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use.
Decarboxylation: Transforming THCA into THC
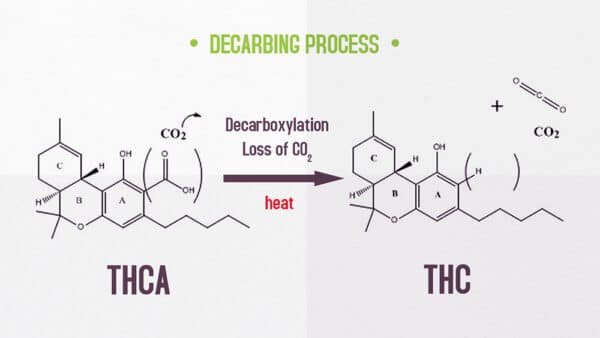
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that “removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2).”
In the cannabis industry, the conversion of THCA to THC is called decarboxylation. It’s easy to understand; we discussed that THCA has an extra carboxyl, which makes it unfit for interacting with the cannabinoid receptors of the brain. During decarboxylation, this extra carboxyl is removed from the THCA molecule, converting it to a THC molecule and unlocking the psychoactive potential of cannabis. This is why eating raw cannabis doesn’t produce a high, but consuming cannabis-infused edibles does.
Decarboxylation explains the difference between THC and THCA in terms of their effects on the human body. The decarboxylation process plays a crucial role in transforming THCA into THC, unlocking its psychoactive effects. For a deeper look into how THCA is extracted and distilled, read our blog on THCA Distillate: Exploring Cannabis Distillation and Extraction.
THC's Psychoactive Effects
THC is famous because of its psychoactive effects on the body. By binding to the cannabinoid receptors of the brain, particularly the CB1 receptors, THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system. This is how they produce the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use. By affecting the endocannabinoid cycle, THC can alter perception and cause euphoria, relaxation, and increased appetite.
The effects of consuming THC can vary widely depending on the individual, dosage, and method of consumption. While many users enjoy these effects for recreational purposes, THC also has potential therapeutic applications, such as pain relief and nausea reduction.
THCA's Potential Health Benefits

THCA, while not psychoactive, still has potential health benefits that are part of emerging research on its significant therapeutic applications. Due to their chemical composition and as a precursor to THC, THCA could have anti-inflammatory properties, which might be beneficial for conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel diseases.
One of the emerging uses of THCA is as a neuroprotectant. THCA can potentially benefit against neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, it has shown antiemetic (anti-nausea) properties and potential to stimulate appetite. Doctors are considering the use of THCA-based medication to manage chemotherapy-related side effects in cancer patients. In addition to its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, THCA shares some therapeutic similarities with CBD. To explore the key differences between these two cannabinoids, you can check out our in-depth comparison THCA vs. CBD: Key Differences.
THCA vs. THC: How They Work in the Body
THC vs THCA effects vary because they interact differently with the body, particularly with the endocannabinoid system.
Due to its molecular structure, THC directly binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors, primarily in the brain and central nervous system. It makes it a potent psychoactive compound able to alter the psychological state of the consumer. However, THCA doesn’t bind effectively to these receptors due to its larger molecular size. Instead, it shows its effect on the body by working through other mechanisms, such as interacting with the TRPA1 receptor, which is involved in inflammatory processes. This is the reason why THCA can’t produce “a high” effect like THC but may still offer therapeutic benefits.
Key Differences Between THC and THCA
What is THCA vs THC difference is a multifaceted comparison:
- Chemical Structure: As mentioned, THCA has an extra carboxyl group that THC lacks. This molecular difference in their chemical structure significantly varies their effects on the body.
- Psychoactive Properties: THC is psychoactive, producing a “high” as it can bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain and central nervous system. THCA, due to its chemical structure’s incompatibility with these receptors, is non-psychoactive in its raw form, such as in juices or raw cannabis preparations.
- Health Benefits and Usage: While THC is known for its pain-relieving, appetite-stimulating, and mood-altering effects, THCA has therapeutic benefits ranging from potential anti-inflammatory to neuroprotective properties.
These benefits also result from the way these compounds are consumed. If users are not using active THC, then consuming THCA through smoking or vaping converts it to THC. THCA, which is found in raw cannabis, is often consumed as edibles.
How to Use THCA and THC: Product Types & Dosage
Both THCA and THC are available for consumers in various product forms. These products differ in their consumption methods. THCA products are consumed in raw form to preserve their unique properties.
The most common THCA products include:
- Raw cannabis leaves and flowers
- THCA tinctures
- THCA crystalline
- Raw cannabis juices
These products are natural formulations that deliver THCA without converting it to THC through heat.
THC products, on the other hand, are highly diverse and widely available in legal markets. It includes most processed products:
- Dried cannabis flower for smoking or vaping
- THC oils and tinctures
- Edibles such as gummies, chocolates, and baked goods
- Topical creams and balms
- Concentrates such as wax, shatter, and live resin
Dosage recommendations for THC consumption vary widely depending on the product type, individual tolerance, and desired effects. For beginners, the safe dosage of THC is typically 2.5-5mg. They can gradually increase dosage as needed to prevent side effects. THCA dosages are less standardized due to limited research, but users are advised to start with small amounts of raw cannabis or THCA-rich products.
THCA vs. THC: Legality
The legal framework surrounding THCA vs THC is complex and evolving. In the United States, more and more States are legalizing cannabis, while at the federal level, THC remains Scheduled I Substances, making it illegal. However, hemp-derived THC (containing less than 0.3% THC by dry weight) was legalized under the 2018 Farm Bill.
THCA exists in a legal gray area as it is not explicitly scheduled, but it can be considered an analog of THC. This potentially makes it illegal under the Federal Analogue Act.
State laws vary significantly. Some states have fully legalized both recreational and medical cannabis, including THC and THCA products, while others still have a ban on their recreational use. Consumers should be aware of the local laws before using any THC or THCA product, as a few states still maintain complete prohibition of cannabis and its derivatives.
THCA vs. THC on Drug Tests
During drug testing, THCA can potentially trigger positive results, the same as THC. Most standard drug tests typically detect THC metabolites in urine or blood. While THCA itself is non-psychoactive, these tests can detect it. This is because THCA can easily convert to THC in the body, especially when exposed to heat (such as during smoking), which can then be metabolized and detected.
This raises concerns for individuals using raw cannabis or THCA products for their potential health benefits. While these products may not cause psychoactive effects, they may still test positive on a drug screening.
THCA vs. THC: Potency Comparison
It is a complicated comparison to measure THCA vs THC potency. Both the cannabinoids have their respective effects.
If we make the psychoactive effect as a measure, then THC is undoubtedly more potent than THCA. While even small amounts of THC can induce noticeable psychoactive changes, THCA doesn’t produce any intoxicating effects in its raw form.
But if we talk about potential therapeutic benefits, the comparison gets tricky. THCA can potentially have more potent anti-inflammatory effects than THC. Additionally, because THCA doesn’t cause intoxication, it is preferred by individuals seeking therapeutic benefits without the “high.”
Purely from a scientific outlook, THCA, when fully decarboxylated, converts to THC at a ratio of approximately 0.877:1. It simply means cannabis strains with high THCA content have the potential to be very potent THC when heated, as 87% of the THCA can convert to THC.
THCA vs. THC: Side Effects
Like every other cannabinoid, THCA and THC can cause side effects if abused. However, THC, due to its psychoactive nature, can produce a range of side effects, including:
- Anxiety or paranoia
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
- Impaired memory and concentration
- Increased heart rate
- Dizziness
- In some cases, nausea or vomiting
These side effects are dose-dependent and vary based on individual sensitivity and tolerance.
THCA, being non-psychoactive, has fewer reported side effects. Some users report mild digestive discomfort when consuming large amounts of raw cannabis. However, high consumption of THCA can potentially be dangerous as it can convert to THC in the body when metabolized.
Conclusion
The THCA vs THC debate is an industry- and market-wide discussion. For individuals considering cannabis for recreational or medicinal purposes, it is crucial to understand the difference between THCA and THC.
THC is known for its psychoactive effects, but THCA has potential therapeutic benefits without the high. With an understanding and awareness of the safe consumption methods and dosage, both THC and THCA can be used for a range of benefits. Whether you’re considering THC or THCA, it’s essential to know about local laws and regulations surrounding cannabis use.