Producers can offer several types of concentrates today with the evolution of extraction techniques and equipment. These potent cannabis concentrates provide consumers more options than ever before. There have never been more diverse products for experiencing cannabis. However, this abundance of different types of concentrates makes it essential that consumers understand their unique characteristics, production methods, and uses.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about different types of cannabis concentrates.
Sections
ToggleWhat Are Cannabis Concentrates?
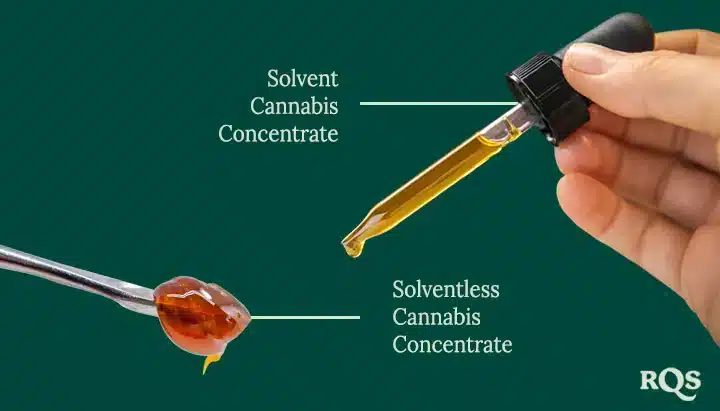
Cannabis concentrates are potent extractions containing a high percentage of cannabinoids and terpenes. The concentrates are created by refining and separating target compounds from the plant material.
How They’re Made
- Solvent-Based: This method uses butane, propane, CO2, and ethanol solvents to dissolve cannabinoids and terpenes from plant material.
- Solventless: These techniques use mechanical or physical means like pressure, temperature, and filtration to produce cannabis concentrate.
Types of Cannabis Concentrates
1. Shatter

Texture: Brittle, glass-like, translucent
Potency: Very high (70-90% THC)
Best For: Dabbing, vaping
Explanation: Explanation: One of the most recognized forms of cannabis concentrate, shatter, is a translucent, brittle concentrate that has an amber appearance. It is produced using hydrocarbon solvents from high quality cannabis plant material.
2. Wax

Texture: Soft, malleable, opaque
Use: Dabbing, vaporizing
Explanation: Wax is the most versatile type of concentrate used in various applications. Wax concentrate’s soft and pliable consistency comes from whipping it during production, introducing air into the mixture, and creating its distinctive, non-transparent appearance.
3. Budder

Texture: Creamy, butter-like
Flavor: Highly rich terpene profile
Explanation: A much smoother form of wax, budder has a smooth, creamy consistency similar to actual butter. It is produced using solvent-based extraction like butane hash oil (BHO) or CO2 oil and agitating the extracts during purging.
4. Crumble

Texture: Dry, crumbly, honeycomb structure
Use: Dabbing, eatables
Explanation: Crumble is a drier cannabis concentrate known for its dry, powder-like texture. It is one of the most common types of concentrate used for adding cannabis to eatables. It is produced by purging the cannabis extracts at low temperatures for a long time, resulting in a distinctively dry, crumbly texture.
5. Sauce

Texture: Viscous liquid, crystalline structure
Flavor: Exceptional terpene content
Explanation: Cannabis sauce is a popular type of concentrate known for its strong flavor profile. This concentrate has a terpene-rich liquid base with THCA crystalline structures suspended throughout, produced using solvent-based extraction.
6. Sugar

Texture: Wet, crystalline, sugar-like
Balance: Potency and flavor
Explanation: Sugar concentrates get their name for their resemblance to wet sugar. With a glistening crystalline appearance, these cannabis concentrates offer an appealing balance between potency and terpene profile.
7. Live Resin

Made From: Fresh frozen cannabis
Terpenes: Exceptionally high preservation
Explanation: Live resin is produced from frozen cannabis using a mix of propane and butane as a solvent. It has one of the highest terpene profiles compared to different types of cannabis concentrates. Due to the perseveration of cannabis at low temperatures, more terpenes are maintained in live resin.
8. Live Rosin

Extraction: Solventless, heat and pressure
Cleanliness: No chemical residue
Explanation: Live rosin is known for its purity as it is produced solventless from fresh cannabis flowers. It maintains high terpene levels while avoiding any chemical residue. Live rosin is a clean, flavorful concentrate free from any potential solvents.
9. Distillate

Form: Clear, viscous oil
Purity: Isolated cannabinoids (up to 99%)
Use: Vape cartridges, edibles
Explanation: Cannabis distillate is a highly refined form of extract produced by molecular distillation, separating specific cannabinoids. The final extract is a highly potent, almost pure form of THC or CBD. However, there are no terpenes present in distillates.
10. Hash (Traditional and Modern)

Forms: Pressed, bubble hash, temple balls
Use: Smoking, vaporizing
Explanation: An original type of concentrate, hash is a cannabis product that has existed for thousands of years. Traditionally, it was produced by physically separating trichomes from plant material and compressing them into blocks or balls. However, modern production techniques use ice-water agitation for more refined separation.
11. Kief

Form: Fine trichome powder
Use: Bowl-topping, hash production
Explanation: Kief is the simplest form among all types of concentrates. It consists of trichome glands that naturally separate from the cannabis flower. This powder is collected using screens or grinders, allowing an easy and more accessible concentrate for most consumers.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of cannabis concentrates is beneficial for consumers. It helps them choose the right kind of cannabis concentrate based on the extraction method, use, form, and potency.
Whether you prioritize flavor, potency, purity, or versatility, there’s a concentrate designed to deliver that ideal experience. With the evolution of the extraction methods in the cannabis industry continuing to mature, we can expect more concentrate types.




