Terpenes are the source material for some of the most versatile cannabis products. These aromatic hydrocarbons add the distinct scent and flavors to the cannabis plants. With more states legalizing cannabis, the demand for high-quality terpene extract has skyrocketed. In this guide on the terpene extraction process, we will explore traditional and cutting-edge methods to obtain these compounds.
Sections
ToggleUnderstanding Terpenes
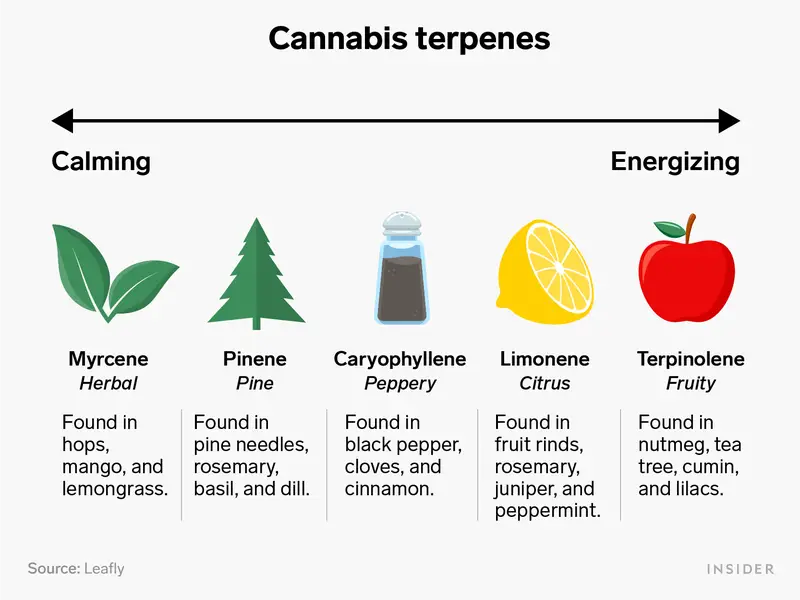
Terpenes are among the most widely occurring compounds in various plants, including conifers, citrus fruits, and cannabis. They serve various natural purposes, from protecting plants from herbivores to attracting pollinators. In cannabis, terpenes are essential for adding a defining aroma and other potential therapeutic effects of different strains. For cannabis enthusiasts and medical users, terpenes add the entourage effect. These compounds enhance the therapeutic and entourage benefits of cannabinoids. This is the reason why terpene extract should be high-quality and well-preserved.
Methods of Terpene Extraction: From Traditional to Advanced Techniques
Depending on the scale and quality of the product you want, you can choose between traditional or advanced techniques. Each extraction method comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
1. Traditional Extraction Methods
a. Steam Distillation

Steam distillation is a traditional method used for centuries to extract terpenes. In this process, steam is passed through plant material in a chamber, vaporizing terpenes as they have low boiling points. Then, these vapors are condensed into an oil-water mixture and later separated.
Advantages:
- A highly cost-effective and relatively simple process
- Suitable for large-scale production
- Produces pure terpene extract without the use of solvents
Disadvantages:
- Steam requires high temperatures that can degrade heat-sensitive terpenes
- Yield is lower than compared to some modern methods
- This terpene extraction method is time-consuming
Steam distillation is widely used across industries, mainly to extract terpenes from aromatic plants for essential oils, perfumes, and food flavorings.
b. Cold Press Extraction
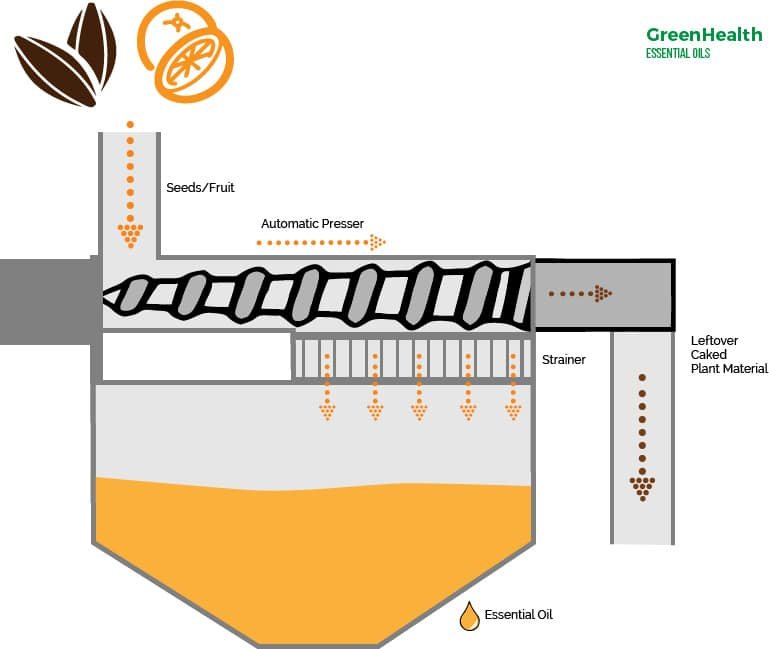
Cold press terpene extraction involves mechanically pressing cannabis plant material to release its oils and terpenes. The process uses a simple mechanical device using two metallic plates pressing plant materials between them to extract essential oils rich in terpenes.
Advantages:
- As there is no heat involved, cold-press terpene extraction preserves heat-sensitive terpenes
- Solventless process ensuring pure terpene profile
- The process is a simple process, with minimal equipment required
Disadvantages:
- Oil extraction is limited to plants with high content
- Lower yield compared to other methods
- Not suitable for all plant materials
The food and beverage industry primarily uses cold press extraction to extract citrus-based terpenes.
2. Solvent-Based Extraction Methods
On an industrial scale, solvent-based extraction methods are utilized for faster large-scale production.
a. Ethanol Extraction

In this process, the cannabis plant material is soaked in high-proof ethanol to dissolve the terpenes. The solvent-terpene solution is then separated, and ethanol is separated by applying heat to evaporate the solvent. The concentrated cannabis with high terpene content is left behind.
Advantages:
- Efficient at extracting a wide range of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Relatively safe solvent with low toxicity
- It can be performed at low temperatures, preserving heat-sensitive terpenes
Disadvantages:
- The process also extracts unwanted compounds like chlorophyll
- It requires post-processing to remove residual ethanol
- It is a costly process due to the need for high-purity ethanol
Ethanol extraction is widely used in the cannabis industry for producing full-spectrum extracts and in the production of herbal tinctures.
b. Butane and Propane Extraction (BHO/PHO)

Also known as hydrocarbon extraction, this process uses butane or propane as solvents to isolate terpenes and cannabinoids from plant material. The solvent-content solution is then purged of the solvent, typically using heat and vacuum.
Advantages:
- BHO and PHO extraction is highly efficient in extracting terpenes
- Known to produce highly potent terpene profile
- It can be performed at low temperatures to preserve volatile compounds
Disadvantages:
- Hydrocarbons are highly flammable, complicating the process
- Requires specialized equipment and trained operators
- Requires post-processing, making the process expensive
The BHO and PHO extraction process is popular in the cannabis industry for producing concentrates like shatter, wax, and live resin.
3. Advanced Extraction Techniques
With the evolution of technology, there are advanced extraction techniques for improved product quality and quantity.
a. Supercritical CO₂ Extraction
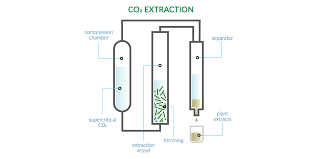
In this process, carbon dioxide is used in a supercritical state as a liquid and a gas. The pressurized and heated CO2 is passed through plant material to dissolve terpenes. The pressure is then reduced, allowing the CO₂ to return to a gas state and evaporate, leaving behind the extracted terpenes. (for a detailed guide on supercritical CO2 extraction, see this post).
Advantages:
- It can be used for highly selective terpene extraction
- CO2 is inert and leaves no toxic residues
- Operates at lower temperatures, preserving heat-sensitive terpenes
- Environmentally friendly and sustainable
Disadvantages:
- High initial equipment cost
- The process is complex and requires skilled operators
- Requires high equipment maintenance
Supercritical CO₂ extraction is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cannabis industries for producing high-purity extracts.
b. Advanced Hydrocarbon Extraction Using Hexane or Pentane

This process is similar to butane extraction but uses hydrocarbons like hexane or pentane to dissolve and extract terpenes from plant material.
Advantages:
- The advanced hydrocarbon extraction method is ideal for non-polar compound terpenes
- Can produce high-yield extracts
- Relatively low boiling points for easy solvent removal
Disadvantages:
- Safety concerns due to the flammability of hydrocarbons
- Strict regulations around use and disposal
- Potential for residual solvent contamination
The applications are similar to other hydrocarbon extraction methods but for large-scale terpene extraction, particularly in the fragrance and flavor industries.
c. Ultrasonic Extraction

Ultrasonic terpene extraction uses high-frequency sound waves. The ultrasonic waves are passed through the solvent and plant material mixture, which creates cavitation bubbles in the solvent, which collapse and create micro-jets that penetrate plant material and release terpenes.
Advantages:
- It is a much faster process as compared to traditional methods
- It does not require heat, making it ideal for heat-sensitive compounds
- Requires less solvent than conventional extraction methods
Disadvantages:
- Less efficient for large-scale production
- Initial equipment costs can be high
- Sonic energy can degrade some terpenes
Ultrasonic extraction is famous for research settings and small-scale production of high-value terpene extracts.
d. Microwave-Assisted Extraction

Similar to ultrasonic extraction, this technique uses microwave energy. The microwaves heat the internal water in plant cells, causing them to burst and release their contents, including terpenes, into a surrounding solvent.
Advantages:
- Fast process resulting in rapid extraction
- Requires less solvent than traditional methods
- More energy-efficient terpene extraction than conventional heating methods
Disadvantages:
- Thermal degradation of heat-sensitive compounds
- Not practical for all plant materials
- Scaling the process to industrial levels can be challenging
Due to its potential in rapid, small-scale extraction, microwave-assisted terpene extraction is generally limited to research and development settings.
e. Enzymatic Extraction

Enzymatic extraction uses select enzymes to break down plant cell walls, releasing terpenes and other compounds. This process is seldom used alone and is often combined with different extraction techniques to improve yield and efficiency.
Advantages:
- Can improve the selective extraction capabilities of other process
- Can assist in extracting delicate compounds
- Environmentally friendly and biocompatible
Disadvantages:
- Enzymes are costly
- Extraction time can be longer compared to other methods
- Requires extensive knowledge of research to handle enzymes
Enzymatic extraction, associated with another process, can help produce high-purity terpene extracts, particularly in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
New and Emerging Techniques
Innovation continues in the terpene extraction domain, with companies like Root Sciences pushing the limits of industrial equipment manufacturing and research. New techniques like Pulsed Electric Field Extraction and Subcritical Water Extraction methods are becoming mainstream. These techniques focus on improving the terpene extraction process’s efficiency while minimizing solvents’ use.
Factors Affecting Terpene Extraction and Purity
The extraction method alone doesn’t determine the quality of terpene extract. Aspiring producers should understand and optimize the factors affecting terpene extraction yield and purity.
1. Plant Material Quality
It all starts with the quality of the source plant material. The quality of terpenes depends on genetics, growing conditions, harvesting time, and post-harvest handling of plants. Genetic factors such as plant strains and varieties affect the natural terpene profiles. Also, drying and storage of plant material are crucial to preserve terpenes.
2. Temperature and Pressure Settings
As terpenes are highly sensitive, temperature and pressure during extraction can significantly impact the yield and quality of terpene extracts. While high temperature can increase extraction efficiency, it may also lead to degradation or alteration of delicate terpenes. Pressure control is also necessary to target specific compounds, allowing for more precise extraction of desired terpenes.
3. Choice of Solvent and Equipment
Several solvents can be used for terpene extraction, and choice depends on varying affinities of solvents for specific terpenes. Solvents like ethanol can extract many compounds, while non-polar solvents like hydrocarbons are excellent for terpene extraction. The precision and reliability of extraction equipment can significantly impact the consistency and quality of terpene extracts. Good quality and well-maintained equipment are crucial and essential for producing pure, contaminant-free extracts.
4. Post-Extraction Handling
Terpene extract quality can also be affected post-extraction. That’s why post-processing steps like solvent removal are essential. Also, the storage conditions must be well-maintained, as terpenes are sensitive to light, heat, and oxygen.
Optimizing the Terpene Extraction Process for Maximum Yield
Whatever terpene extraction process you choose, there are several steps that you can choose to maximize yield. Let’s have a look at some optimization tips.
1. Temperature Optimization
Terpenes are highly sensitive, so you should always begin with lower temperatures to preserve volatile terpenes. While efficiency will be low, you can gradually increase the temperature to improve yield.
2. Pressure Adjustments
In methods like supercritical CO₂ extraction, you might need to optimize pressures through trial and error to find the optimal pressure settings for specific terpene profiles. Implementing staged pressure changes during extraction is best for extraction.
3. Extraction Duration
Producers have to balance time and yield for optimized outcomes. While longer extraction times can increase yield, they may also lead to degradation.
4. Solvent-to-Material Ratio
Different solvent-to-plant ratios are tested in solvent terpene extraction to find the most efficient balance between yield and solvent use. You can consider recirculating the solvent into the system to improve extraction efficiency without increasing solvent volume.
5. Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
Well-calibrated and maintained equipment is essential to maintain high yield. Invest in terpene extraction equipment like those offered by Root Sciences that employ modern pressure and temperature sensors that can automatically control these parameters. Also, a rigorous maintenance schedule should be implemented to prevent equipment failures, and equipment should be cleaned between extractions to avoid cross-contamination and to maintain consistency.
The Main Issue with Terpene Extraction
The most volatile and aromatic terpenes (monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes) are typically lost to the extraction solvent during solvent recovery or off-gassing or thermally degrade in subsequent post-processing steps, forming foul smelling compounds.
In a conventional extraction and distillation process flow, the terpene fraction from Root Sciences’ wiped-film molecular distillation machines contain valuable diterpenes and triterpenes as well as some cannabinoid content and is, therefore, a valuable process stream.
However, due to their thermally sensitive nature, any monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes would degrade into foul smelling contaminants that are removed. Regardless, the first pass terpene distillate is often used in conjunction with other terpenes, either non-cannabis derived botanical terpenes purchased from a third party, or cannabis derived terpenes. This results in an incomplete terpene profile that lacks the pungent aromatics that give each strain their unique aroma and flavor.
Any effort to preserve terpenes requires differential extraction techniques, such as subcritical CO2 extraction, or cold-hydrocarbon extraction. These techniques can produce terpene rich extracts, but significantly diminish the throughput of a processing lab’s beating heart – the extractor.
In addition to reduced productivity, these techniques still require the use of solvents to extract terpenes, and therefore incur significant losses of the most volatile terpenes during the solvent recovery stage.
The Solution: STX 90 Solventless Terpene Extractor

Enter the STX 90 Solventless Terpene Extractor. By directly evaporating the most valuable aromatics straight from the biomass prior to conventional extraction, these prized molecules can be preserved, and the biomass processed as usual. The terpenes can then be recombined with the concentrates or distillates, resulting in a full spectrum, terpene rich product that resembles the original biomass as closely as possible.
As it is a solventless separation technique, the terpene isolate created by the STX 90 is unrivaled in quality, aroma, and authenticity. With no loss of valuable volatiles during a solvent recovery step, the terpene profile – a unique fingerprint that differs from strain to strain – is perfectly preserved.
When mixed with first pass terpene distillate, a complete and unadulterated terpene distillate can be achieved. This is an excellent ingredient to add to second pass cannabinoid distillate to produce completely cannabis derived solventless terpene vape pens or innumerous other products.
Regardless of which extraction methodology is utilized, the STX 90 Solventless Terpene Extractor will ensure that the unique terpene fingerprint and therapeutic entourage effects of your carefully grown biomass are preserved.
A small amount of these terpenes can be used to create many, many vape cartridges, so only a small fraction of the biomass needs to be processed in this way. There is no degradation to the biomass during this process, and it can be extracted as normal afterwards, so this equipment can be seamlessly integrated into your process.
Find the Ideal Solventless Terpene Extractor for Your Business
Other Challenges in Terpene Extraction
Let’s explore some of other challenges associated with terpene extraction that can help you avoid common pitfalls and maintain high purity and yield.
1. Purity and Contamination Issues: Several factors can lead to contamination, and maintaining the purity of terpene extract can be challenging. Develop more selective extraction methods and refine purification techniques.
2. Thermal Degradation: Terpenes are heat-sensitive, and thermal degradation is a prominent reason for poor product quality. Maintain low-temperature processes to minimize thermal degradation during extraction and post-processing.
3. Complex Extraction Processes: Advanced extraction methods like hydrocarbon extraction are complex and require specialized knowledge and equipment. Utilize Root Sciences equipment to simplify these processes without compromising quality.
4. High Cost of Equipment: Equipment required for processes like supercritical CO₂ extraction has a high initial investment cost. It can prove to be prohibitive for smaller operations.
5. Scalability Concerns: Producers must consider scaling up production while maintaining quality and consistency when deciding on equipment and extraction methods. Your small-scale production can face several challenges at a larger scale.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Depending on the materials used for terpene extraction, you have to deal with regulatory challenges. Adhering to regulations and compliance, especially in the cannabis industry, can be challenging and resource-intensive.
7. Maintaining Terpene Profile Consistency: If you are not tracking and recording the terpene extraction process, achieving consistent terpene profiles will be challenging. Factors like plant variability, seasonal changes, and subtle differences in extraction parameters can all impact the final terpene profile.
Applications of Terpenes: Beyond Cannabis

Terpene extraction is not limited to the cannabis industry but has a broad scope across several sectors. Here are some of the industrial applications of terpenes beyond cannabis.
- Aromatherapy and Essential Oils
Terpenes, due to their aroma profile, are the primary ingredients of aromatherapy and essential oil products. Due to the association of their aromatic properties with various psychological and physiological effects, terpenes are known to promote relaxation, focus, or energy. - Perfumes and Fragrances
The fragrance industry heavily relies on natural terpenes to create complex scent profiles. From floral and fruity to woody and spicy, terpene profiles are crucial for many popular perfumes and colognes. - Food and Beverages
Natural terpene extracts are also used to flavor and add aroma to many foods and beverages. Terpenes add unique flavors, from soft drinks to candies, particularly in the craft beer industry. - Pharmaceuticals and Therapeutics
Due to their potential therapeutic properties, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antimicrobial effects, pharmaceutical companies also use terpenes. These benefits of terpenes are also being researched for drug development and as natural alternatives to synthetic compounds. - Cleaning Products
Due to their antimicrobial properties, certain terpenes are used to manufacture natural cleaning products. Terpenes like limonene in citrus fruits are often used in eco-friendly household cleaners. - Insect Repellents
Terpenes help plants to repel insects. The presence of some terpenes, such as citronellol and geraniol, act as natural insect repellents, which is why they are used in outdoor candles, sprays, and lotions. - Skincare and Cosmetics
Studies have shown that terpenes have antioxidant and anti-aging properties. This is why they are incorporated into many skincare and cosmetic products for their aromatic properties and potential benefits to skin health.
Future Prospects
As a producer, it is important to track future terpene extraction methods and equipment prospects. It involves tracking:
1. Advancements in Extraction Technologies: Keep track of new extraction methods and refine existing techniques, such as pulsed electric field extraction and subcritical water extraction. These technologies hold the potential for more sustainable and efficient terpene extraction.
2. Growing Demand in Various Industries: Given the diverse terpene profile and increasing recognition across multiple industries, the demand for high-quality extracts is rising.
3. Increased Focus on Sustainable Extraction: The sustainable extraction process requires addressing environmental concerns. You should select methods to reduce solvent use, minimize energy consumption, and explore bio-based extraction techniques.
4. Development of Synthetic Terpenes: Research is being done in biotechnology science to produce synthetic terpenes through fermentation and other processes. For producers, this could mean sourcing a more consistent and scalable source of terpenes.
5. Expansion into New Applications: In fields like medicine, materials science, and agriculture, the application of terpenes is increasing. This expansion is likely to drive further innovation in extraction and purification techniques.
6. Research on Terpene Synergy and Benefits: As research into understanding how different terpenes interact with each other and with other plant compounds is growing, it could lead to more targeted extraction methods.
7. Enhanced Quality Control and Standardization: As terpene extraction becomes mainstream, you can expect more standardized terpene analysis and quality control methods.
Sustainability in Terpene Extraction: Greener Practices
One of the challenges that terpene extraction faces is how to keep the process sustainable, particularly in industries like cannabis and pharmaceuticals. The increasing demand for quality terpene extracts and focus on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices is causing a shift towards greener extraction methods.
The primary area of focus is on reducing solvent waste. During solvent extraction methods, volatile and flammable solvent residue is a significant source of contamination. Producers can take steps such as solvent recycling, alternative solvents, and solvent-free methods for reducing waste. Also, utilizing heat recovery systems, designing extraction systems to minimize energy use, and using renewable energy sources can boost greener practices.
Furthermore, focusing on waste reduction and utilization methods is essential, such as finding uses for spent plant material after extraction, turning waste products into valuable inputs for other industries, and encouraging and supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
Conclusion
Terpene extracts make the basis for several products across industries. The growing understanding of these versatile compounds increases demand for a more comprehensive terpene profile. Producers can choose from several extraction methods, from steam distillation to cutting-edge techniques such as supercritical CO₂ extraction. However, it is essential to consider the requirements and challenges of each technique.
Our guide provides a comprehensive overview of each extraction method, optimization of existing processes, and applications of terpenes beyond the cannabis industry.




